The Associations between Sibling Victimization, Sibling Bullying, Parental Acceptance-Rejection, and School Bullying
- PMID: 36498416
- PMCID: PMC9739229
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192316346
The Associations between Sibling Victimization, Sibling Bullying, Parental Acceptance-Rejection, and School Bullying
Abstract
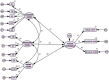
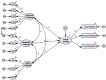
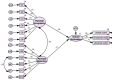
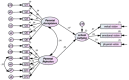
Bullying has been identified as the most common form of aggression experienced by school-age youth. However, it is still unclear about the family's influence on school bullying. Therefore, the current study aimed to explore the associations between sibling bullying and school bullying, sibling victimization and school victimization, and parental acceptance-rejection and school bullying victimization. The study was cross-sectional and conducted on a sample of students aged between 11 and 20 years recruited from middle schools in Algeria. The study used a survey adopted from the scale of Sibling Bullying, Student Survey of Bullying Behavior-Revised 2, and the Survey of parental acceptance-rejection in collecting the data. The model's results assessing the association between sibling bullying and school bullying demonstrated that the effect of sibling physical and sibling verbal victims on school victimization was statistically significant. Despite the non-significant effect of sibling emotional victims on school victimization, the effect of sibling physical and sibling verbal bullying on school bullying was statistically significant. However, the effect of sibling emotional bullying on school bullying was not statistically significant. The direct effect of parental acceptance on school victimization was not statistically significant, whereas the effect of parental rejection on school victimization was statistically significant. The direct effect of parental acceptance on school bullying was not statistically significant, while the effect of parental rejection on school bullying was statistically significant. Based on the results, this study provides insights into the understanding of how the family and siblings contribute to school bullying. In particular, sibling victimization, sibling bullying, and parental acceptance-rejection are predictive factors of school bullying among adolescents. Future research should take into account factors based on family to explore the risks of school bullying.
Keywords: adolescent students; children’s health; parental acceptance and rejection; school bullying; sibling bullying; violence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang H., Jiang Y. A Systematic Review of Research on School Bullying/Violence in Mainland China: Prevalence and Correlates. J. Sch. Violence. 2022;21:48–59. doi: 10.1080/15388220.2021.1985326. - DOI
-
- Nadhiroh S., Nurmala I., Pramukti I., Tivany S., Tyas L., Zari A., Poon W., Siaw Y.-L., Kamolthip R., Chirawat P., et al. Weight stigma in Indonesian young adults: Validating the indonesian versions of the weight self-stigma questionnaire and perceived weight stigma scale. Asian J. Soc. Health Behav. 2022;5:169–179. doi: 10.4103/shb.shb_189_22. - DOI
-
- Pengpid S., Peltzer K. Anxiety-induced sleep disturbances among in-school adolescents in the United Arab Emirates: Prevalence and associated factors. Asian J. Soc. Health Behav. 2022;5:18–23. doi: 10.4103/shb.shb_120_21. - DOI
-
- Smokowski P.R., Evans C.B. Bullying and Victimization Across the Lifespan. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2019. pp. XIV, 286.
-
- Sapouna M. Bullying. In: Bruinsma G., Weisburd D., editors. Encyclopedia of Criminology and Criminal Justice. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2014. pp. 223–231.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

