Measurements of Anterior and Posterior Corneal Curvatures with OCT and Scheimpflug Biometers in Patients with Low Total Corneal Astigmatism
- PMID: 36498495
- PMCID: PMC9736849
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11236921
Measurements of Anterior and Posterior Corneal Curvatures with OCT and Scheimpflug Biometers in Patients with Low Total Corneal Astigmatism
Abstract
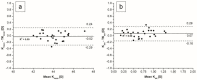
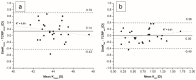
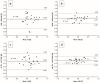
Background: Posterior keratometry measurements are evolving features of the optical biometers. The differences between devices have bigger impact for the low astigmatism values. The majority of adults present the corneal astigmatism below 1.5 D. Objectives: To compare the total corneal astigmatism measured with two different technologies in cataract patients with corneal astigmatism below 1.5 D. Material and Methods: Three automated exams were performed on each of the two devices: swept-source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) and Scheimpflug biometers. The anterior and total corneal astigmatism and power were analysed. Statistical comparisons were performed for within-subject standard deviation, repeatability, Bland−Altman and vector analysis. Results: Twenty-nine eyes of twenty-seven patients were included. The limits of agreement between anterior and total corneal astigmatism were narrower for the SS-OCT than for the Scheimpflug biometer (−0.16 to 0.29 D and −0.40 to 0.39 D, respectively). The >0.5 D difference between SS-OCT and Scheimpflug total astigmatism was noticed in 5 (17%) of cases. The difference between mean total keratometric power for both devices was statistically significant (0.2 D, p < 0.001). SS-OCT total corneal flat measurements had worse repeatability than Scheimpflug (p = 0.007). Conclusions: For the corneal astigmatism <1.5 D, the difference between anterior and total corneal astigmatism measured with SS-OCT was clinically not significant. The mean anterior and total keratometry values obtained with Scheimpflug and SS-OCT biometers are not interchangeable.
Keywords: astigmatism; keratometry; posterior cornea.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparison of total keratometry with corneal power measured by optical low-coherence reflectometry and placido-dual Scheimpflug system.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2022 May;32(3):1496-1503. doi: 10.1177/11206721211020633. Epub 2021 May 29. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 34053330
-
[Comparison of corneal refractive power and astigmatism measured by the new anterior segment optical coherence tomographic device and Scheimpflug imaging device in age-related cataract patients].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Jan 11;57(1):48-55. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112142-20200904-00574. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33412642 Chinese.
-
Repeatability and comparability of keratometry measurements obtained with swept-source optical coherence and combined dual Scheimpflug-Placido disk-based tomography.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2020 Dec;46(12):1637-1643. doi: 10.1097/j.jcrs.0000000000000346. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2020. PMID: 32818349
-
Corneal astigmatism agreement between a swept-source ocular coherence tomography and Scheimpflug-Placido based optical biometers.Int Ophthalmol. 2025 Mar 6;45(1):83. doi: 10.1007/s10792-025-03435-3. Int Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40045024 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Keratometry Obtained by a Swept Source OCT-Based Biometer with a Standard Optical Biometer and Scheimpflug Imaging.Curr Eye Res. 2018 Jul;43(7):882-888. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2018.1458881. Epub 2018 Apr 9. Curr Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 29630418
Cited by
-
Accuracy of Toric Intraocular Lens Calculators with Predicted and Measured Posterior Corneal Astigmatism Across Different Types of Astigmatism.Ophthalmol Ther. 2024 Jul;13(7):1877-1889. doi: 10.1007/s40123-024-00931-0. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Ophthalmol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38581606 Free PMC article.
-
Anterior Segment Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography-based Assessment of Corneal Refractive Profiles in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Patients: A Controlled Comparative Study.Korean J Ophthalmol. 2025 Apr;39(2):103-113. doi: 10.3341/kjo.2024.0106. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40007095 Free PMC article.
-
Repeatability and agreement of a new anterior segment optical coherence tomography with standard devices in normal, keratoconus, and post-refractive eyes.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025 Mar 1;73(3):325-334. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_805_24. Epub 2025 Feb 26. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40007267 Free PMC article.
-
Upper Eyelid Blepharoplasty: Surgical Techniques and Results-Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2023 Oct;47(5):1870-1883. doi: 10.1007/s00266-023-03436-6. Epub 2023 Jul 10. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2023. PMID: 37430010 Free PMC article.
-
Repeatability and Interobserver Reproducibility of a Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography for Measurements of Anterior, Posterior, and Total Corneal Power.Ophthalmol Ther. 2023 Dec;12(6):3263-3279. doi: 10.1007/s40123-023-00815-9. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Ophthalmol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37787889 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

