Left Heart Disease Phenotype in Elderly Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Insights from the Italian PATRIARCA Registry
- PMID: 36498710
- PMCID: PMC9735657
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11237136
Left Heart Disease Phenotype in Elderly Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Insights from the Italian PATRIARCA Registry
Abstract
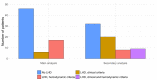
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in the elderly is often associated with left heart disease (LHD), prompting concerns about the use of pulmonary vasodilators. The PATRIARCA registry enrolled ≥70 year-old PAH or chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH) patients at 11 Italian centers from 1 December 2019 through 15 September 2022. After excluding those with CTEPH, post-capillary PH at the diagnostic right heart catheterization (RHC), and/or incomplete data, 23 (33%) of a total of 69 subjects met the criteria proposed in the AMBITION trial to suspect LHD. Diabetes [9 (39%) vs. 6 (13%), p = 0.01] and chronic kidney disease [14 (61%) vs. 12 (26%), p = 0.003] were more common, and the last RHC pulmonary artery wedge pressure [14 ± 5 vs. 10 ± 3 mmHg, p < 0.001] was higher and pulmonary vascular resistance [5.56 ± 3.31 vs. 8.30 ± 4.80, p = 0.02] was lower in LHD than non-LHD patients. However, PAH therapy was similar, with 13 (57%) and 23 (50%) subjects, respectively, taking two oral drugs. PAH medication patterns remained comparable between LHD and non-LHD patients also when the former [37, 54%] were identified by atrial fibrillation and echocardiographic features of LHD, in addition to the AMBITION criteria. In this real-world snapshot, elderly PAH patients were treated with pulmonary vasodilators, including combinations, despite a remarkable prevalence of a LHD phenotype.
Keywords: comorbidity; elderly; left heart disease; pulmonary hypertension; vasodilator.
Conflict of interest statement
P.A. had speaker and/or advisor fees from Janssen and MSD outside the scope of the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Galiè N., Humbert M., Vachiery J.L., Gibbs S., Lang I., Torbicki A., Simmonneau G., Peacock A., Vonk Noordegraaf A., Beghetti M., et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Eur. Heart J. 2016;37:67. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv317. - DOI - PubMed
-
- D’Alonzo G.E., Barst R.J., Ayres S.M., Bergofsky E.H., Brundage B.H., Detre K.M., Fishman A.P., Goldring R.M., Groves B.M., Kernis J.T., et al. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Results from a national prospective registry. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991;115:343–349. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-5-343. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

