Molecular and Pharmacological Characterization of β-Adrenergic-like Octopamine Receptors in the Endoparasitoid Cotesia chilonis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae)
- PMID: 36498840
- PMCID: PMC9740559
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232314513
Molecular and Pharmacological Characterization of β-Adrenergic-like Octopamine Receptors in the Endoparasitoid Cotesia chilonis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae)
Abstract
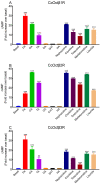
Octopamine (OA) is structurally and functionally similar to adrenaline/noradrenaline in vertebrates, and OA modulates diverse physiological and behavioral processes in invertebrates. OA exerts its actions by binding to specific octopamine receptors (OARs). Functional and pharmacological characterization of OARs have been investigated in several insects. However, the literature on OARs is scarce for parasitoids. Here we cloned three β-adrenergic-like OARs (CcOctβRs) from Cotesia chilonis. CcOctβRs share high similarity with their own orthologous receptors. The transcript levels of CcOctβRs were varied in different tissues. When heterologously expressed in CHO-K1 cells, CcOctβRs induced cAMP production, and were dose-dependently activated by OA, TA and putative octopaminergic agonists. Their activities were inhibited by potential antagonists and were most efficiently blocked by epinastine. Our study offers important information about the molecular and pharmacological properties of β-adrenergic-like OARs from C. chilonis that will provide the basis to reveal the contribution of individual receptors to the physiological processes and behaviors in parasitoids.
Keywords: cAMP; expression profiles; octopamine receptor; parasitoid; pharmacology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Molecular and pharmacological characterization of a β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor from the green rice leafhopper Nephotettix cincticeps.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 May;120:103337. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2020.103337. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32109588
-
Pharmacological characterisation and functional roles for egg-laying of a β-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor in the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Aug;87:55-64. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2017.06.008. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28629966
-
Functional and pharmacological characterization of a beta-adrenergic-like octopamine receptor from the silkworm Bombyx mori.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2010 Jun;40(6):476-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2010.04.007. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20417278
-
Physiological functions and pharmacological and toxicological effects of p-octopamine.Drug Chem Toxicol. 2015 Jan;38(1):106-12. doi: 10.3109/01480545.2014.900069. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Drug Chem Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 24654910 Review.
-
Octopamine--after a decade as a putative neuroregulator.Essays Neurochem Neuropharmacol. 1981;5:47-73. Essays Neurochem Neuropharmacol. 1981. PMID: 6112146 Review.
References
-
- Xu G., Wu S.F., Wu Y.S., Gu G.X., Fang Q., Ye G.Y. De novo assembly and characterization of central nervous system transcriptome reveals neurotransmitter signaling systems in the rice striped stem borer, Chilo suppressalis. BMC Genom. 2015;16:525. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1742-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

