Characterization in Potent Modulation on Voltage-Gated Na+ Current Exerted by Deltamethrin, a Pyrethroid Insecticide
- PMID: 36499059
- PMCID: PMC9737322
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232314733
Characterization in Potent Modulation on Voltage-Gated Na+ Current Exerted by Deltamethrin, a Pyrethroid Insecticide
Abstract
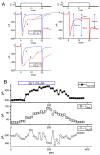
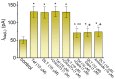
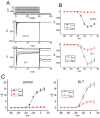
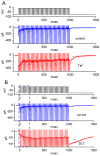
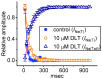
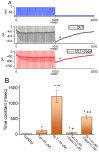
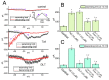
Deltamethrin (DLT) is a type-II pyrethroid ester insecticide used in agricultural and domestic applications as well as in public health. However, transmembrane ionic channels perturbed by this compound remain largely unclear, although the agent is thought to alter the gating characteristics of voltage-gated Na+ (NaV) channel current. In this study, we reappraised whether and how it and other related compounds can make any further modifications on voltage-gated Na+ current (INa) in pituitary tumor (GH3) cells. Cell exposure to DLT produced a differential and dose-dependent stimulation of peak (transient, INa(T)) or sustained (late, INa(L)) INa; consequently, the EC50 value required for DLT-stimulated INa(T) or INa(L) was determined to be 11.2 or 2.5 μM, respectively. However, neither the fast nor slow component in the inactivation time constant of INa(T) activated by short depolarizing pulse was changed with the DLT presence; conversely, tefluthrin (Tef), a type-I pyrethroid insecticide, can accentuate INa with a slowing in inactivation time course of the current. The INa(L) augmented by DLT was attenuated by further application of either dapagliflozin (Dapa) or amiloride, but not by chlorotoxin. During pulse train (PT) stimulation, with the Tef or DLT presence, the cumulative inhibition of INa(T) became slowed; moreover, following PT stimuli, a large tail current with a slowly recovering process was observed. Alternatively, during rapid depolarizing pulse, the amplitude of INa(L) and tail INa (INa(Tail)) for each depolarizing pulse became progressively increased by adding DLT, not by Tef. The recovery time constant following PT stimulation with continued presence of Tef or DLT was shortened by further addition of Dapa. The voltage-dependent hysteresis (Hys(V)) of persistent INa was differentially augmented by Tef or DLT. Taken together, the magnitude, gating, frequency dependence, as well as Hys(V) behavior of INa exerted by the presence of DLT or Tef might exert a synergistic impact on varying functional activities of excitable cells in culture or in vivo.
Keywords: late Na+ current; persistent Na+ current; pyrethroids; transient Na+ current; voltage-gated Na+ current.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors report no declaration that is directly relevant to this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Concerted suppressive effects of carisbamate, an anti-epileptic alkyl-carbamate drug, on voltage-gated Na+ and hyperpolarization-activated cation currents.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 May 24;17:1159067. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1159067. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37293624 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization in Inhibitory Effectiveness of Carbamazepine in Voltage-Gated Na+ and Erg-Mediated K+ Currents in a Mouse Neural Crest-Derived (Neuro-2a) Cell Line.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 17;23(14):7892. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147892. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887240 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization in Effective Stimulation on the Magnitude, Gating, Frequency Dependence, and Hysteresis of INa Exerted by Picaridin (or Icaridin), a Known Insect Repellent.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 26;23(17):9696. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179696. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077093 Free PMC article.
-
Effective Perturbations by Small-Molecule Modulators on Voltage-Dependent Hysteresis of Transmembrane Ionic Currents.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 21;23(16):9453. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169453. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poisoning due to pyrethroids.Toxicol Rev. 2005;24(2):93-106. doi: 10.2165/00139709-200524020-00003. Toxicol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16180929 Review.
Cited by
-
Concerted suppressive effects of carisbamate, an anti-epileptic alkyl-carbamate drug, on voltage-gated Na+ and hyperpolarization-activated cation currents.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 May 24;17:1159067. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1159067. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37293624 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Ionic Mechanisms in Pituitary Cells: Implications for Electrophysiological and Electropharmacological Research.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 30;14(9):3117. doi: 10.3390/jcm14093117. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40364147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ion Channels as a Potential Target in Pharmaceutical Designs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 30;24(7):6484. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076484. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laskowski D.A. Physical and chemical properties of pyrethroids. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002;174:49–170. - PubMed
-
- Dhiman S., Yadav K., Acharya B.N., Nagar D.P., Rao Ghorpade R. Deltamethrin Contact Exposure Mediated Toxicity and Histopathological Aberrations in Tissue Systems of Public Health Importance Cockroach Species Periplaneta americana and Blattella germanica. Front. Physiol. 2022;13:926267. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.926267. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eads D., Livieri T., Tretten T., Hughes J., Kaczor N., Halsell E., Grassel S., Dobesh P., Childers E., Lucas D., et al. Assembling a safe and effective toolbox for integrated flea control and plague mitigation: Fipronil experiments with prairie dogs. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0272419. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272419. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

