What Exactly Is Inflammation (and What Is It Not?)
- PMID: 36499232
- PMCID: PMC9738871
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232314905
What Exactly Is Inflammation (and What Is It Not?)
Abstract
In medicine, inflammation is a fuzzy, overused word first coined by the Romans, the intended meaning and precise definition of which varies according to the person and the clinical context. It tends to carry a negative connotation as a response gone awry, like a raging, out-of-control wildfire that requires immediate control and containment lest it destroy all in its path; however, frequently overlooked or lost in the shuffle is the primordial importance of inflammation to health and survival. The precise definition of inflammation matters for several reasons, not least because of the over-liberal use of anti-inflammatory drugs to inhibit inflammation, which may, contrary to prevailing dogma that all inflammation is harmful, act counterproductively to prevent restitutio ad integrum. Using fire as a central analogy, this overview attempts to define inflammation, the better to determine how to manage it, i.e., whether to fan its flames, let it burn out, or suppress it entirely.
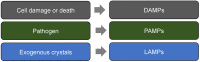
Keywords: DAMPs; LAMPs; PAMPs; SAMPs; immune interventions; inflammation; innate immune cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hannoodee S., Nasuruddin D.N. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. Acute Inflammatory Response. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

