TULA-Family Regulators of Platelet Activation
- PMID: 36499237
- PMCID: PMC9736690
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232314910
TULA-Family Regulators of Platelet Activation
Abstract
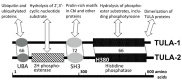
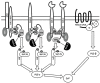
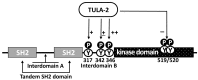
The two members of the UBASH3/TULA/STS-protein family have been shown to critically regulate cellular processes in multiple biological systems. The regulatory function of TULA-2 (also known as UBASH3B or STS-1) in platelets is one of the best examples of the involvement of UBASH3/TULA/STS proteins in cellular regulation. TULA-2 negatively regulates platelet signaling mediated by ITAM- and hemITAM-containing membrane receptors that are dependent on the protein tyrosine kinase Syk, which currently represents the best-known dephosphorylation target of TULA-2. The biological responses of platelets to collagen and other physiological agonists are significantly downregulated as a result. The protein structure, enzymatic activity and regulatory functions of UBASH3/TULA/STS proteins in the context of platelet responses and their regulation are discussed in this review.
Keywords: ITAM; Syk; TULA-2; hemITAM; phosphorylation; platelet; signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TULA Proteins in Men, Mice, Hens, and Lice: Welcome to the Family.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 23;24(11):9126. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119126. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TULA-2 Protein Phosphatase Suppresses Activation of Syk through the GPVI Platelet Receptor for Collagen by Dephosphorylating Tyr(P)346, a Regulatory Site of Syk.J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 21;291(43):22427-22441. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.743732. Epub 2016 Sep 8. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27609517 Free PMC article.
-
TULA-family proteins: Jacks of many trades and then some.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jan;234(1):274-288. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26890. Epub 2018 Aug 4. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30076707 Review.
-
TULA proteins as signaling regulators.Cell Signal. 2020 Jan;65:109424. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2019.109424. Epub 2019 Oct 19. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 31639493 Review.
-
Phosphorylation of (Ser 291) in the linker insert of Syk negatively regulates ITAM signaling in platelets.Platelets. 2024 Dec;35(1):2369766. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2024.2369766. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Platelets. 2024. PMID: 38904212
Cited by
-
TULA Proteins in Men, Mice, Hens, and Lice: Welcome to the Family.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 23;24(11):9126. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119126. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-phased Kinetics and Interaction of Protein Kinase Signaling in Glycoprotein VI-Induced Platelet αIIbβ3 Integrin Activation and Degranulation.Thromb Haemost. 2025 May;125(5):470-483. doi: 10.1055/a-2311-0117. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Thromb Haemost. 2025. PMID: 38653482 Free PMC article.
-
The Ubiquitin-Associated and SH3 Domain-Containing Proteins (UBASH3) Family in Mammalian Development and Immune Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 5;25(3):1932. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031932. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339213 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wattenhofer M., Shibuya K., Kudoh J., Lyle R., Michaud J., Rossier C., Kawasaki K., Asakawa S., Minoshima S., Berry A., et al. Isolation and characterization of the UBASH3A gene on 21q22.3 encoding a potential nuclear protein with a novel combination of domains. Hum. Genet. 2001;108:140–147. doi: 10.1007/s004390000453. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carpino N., Kobayashi R., Zang H., Takahashi Y., Jou S.T., Feng J., Nakajima H., Ihle J.N. Identification, cDNA cloning, and targeted deletion of p70, a novel, ubiquitously expressed SH3 domain-containing protein. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002;22:7491–7500. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.21.7491-7500.2002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

