Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain (NF-L) Is a Prognostic Biomarker for Cortical Damage Evolution but Not for Cognitive Impairment or Epileptogenesis Following Experimental TBI
- PMID: 36499527
- PMCID: PMC9736117
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232315208
Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain (NF-L) Is a Prognostic Biomarker for Cortical Damage Evolution but Not for Cognitive Impairment or Epileptogenesis Following Experimental TBI
Abstract
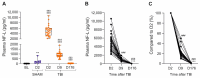
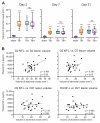
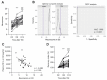
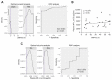
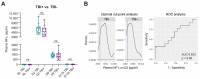
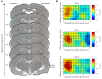
Plasma neurofilament light chain (NF-L) levels were assessed as a diagnostic biomarker for traumatic brain injury (TBI) and as a prognostic biomarker for somatomotor recovery, cognitive decline, and epileptogenesis. Rats with severe TBI induced by lateral fluid-percussion injury (n = 26, 13 with and 13 without epilepsy) or sham-operation (n = 8) were studied. During a 6-month follow-up, rats underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (day (D) 2, D7, and D21), composite neuroscore (D2, D6, and D14), Morris-water maze (D35−D39), and a 1-month-long video-electroencephalogram to detect unprovoked seizures during the 6th month. Plasma NF-L levels were assessed using a single-molecule assay at baseline (i.e., naïve animals) and on D2, D9, and D178 after TBI or a sham operation. Plasma NF-L levels were 483-fold higher on D2 (5072.0 ± 2007.0 pg/mL), 89-fold higher on D9 (930.3 ± 306.4 pg/mL), and 3-fold higher on D176 32.2 ± 8.9 pg/mL after TBI compared with baseline (10.5 ± 2.6 pg/mL; all p < 0.001). Plasma NF-L levels distinguished TBI rats from naïve animals at all time-points examined (area under the curve [AUC] 1.0, p < 0.001), and from sham-operated controls on D2 (AUC 1.0, p < 0.001). Plasma NF-L increases on D2 were associated with somatomotor impairment severity (ρ = −0.480, p < 0.05) and the cortical lesion extent in MRI (ρ = 0.401, p < 0.05). Plasma NF-L increases on D2 or D9 were associated with the cortical lesion extent in histologic sections at 6 months post-injury (ρ = 0.437 for D2; ρ = 0.393 for D9, p < 0.05). Plasma NF-L levels, however, did not predict somatomotor recovery, cognitive decline, or epileptogenesis (p > 0.05). Plasma NF-L levels represent a promising noninvasive translational diagnostic biomarker for acute TBI and a prognostic biomarker for post-injury somatomotor impairment and long-term structural brain damage.
Keywords: ROC analysis; fluid-percussion injury; post-traumatic epilepsy; rat; single molecule array (SIMOA).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

