Mulberry Leaf Supplements Effecting Anti-Inflammatory Genes and Improving Obesity in Elderly Overweight Dogs
- PMID: 36499541
- PMCID: PMC9735752
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232315215
Mulberry Leaf Supplements Effecting Anti-Inflammatory Genes and Improving Obesity in Elderly Overweight Dogs
Abstract
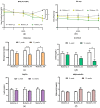
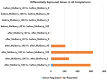
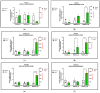
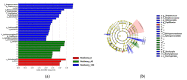
Overweight and obesity, associated with various health complications, refer to abnormal or excessive fat accumulation conditions that harm health. Like humans, obesity is a growing problem in dogs, which may increase the risk of serious diseases such as diabetes and cancer. Mulberry leaf has shown potential anti-obesity and anti-diabetes effects in several studies. Our research studied the impact of mulberry leaf supplements in healthy old overweight dogs for 12 weeks. Blood and fecal samples were collected from the dogs before and after treatment for different analyses, including whole transcriptome and gut microbiome analysis. The Body Condition Score (BCS) and blood glucose levels were significantly decreased in all mulberry treatment groups, which justifies the anti-obesity effect of mulberry leaf in dogs. Throughout the whole transcriptome study, the downregulation of PTX3 and upregulation of PDCD-1, TNFRSF1B, RUNX3, and TICAM1 genes in the high mulberry group were found, which have been associated with anti-inflammatory effects in the literature. It may be an essential gene expression mechanism responsible for the anti-inflammatory and, subsequently, anti-obesity effects associated with mulberry leaf treatment, as confirmed by real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis. In microbiome analysis, Papillibacter cinnamivorans, related to the Mediterranean diet, which may cause anti-inflammatory effects, were abundant in the same treatment group. Further studies may be required to establish the gene expression mechanism and role of abundant bacteria in the anti-obesity effect of mulberry supplements in dogs. Overall, we propose mulberry leaves as a portion of food supplements for improving blood glucose levels and the anti-inflammation of blood in companion dogs.
Keywords: Papillibacter cinnamivorans; anti-inflammation; companion; mulberry leaf; obesity; overweight.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
1-Deoxynojirimycin containing Morus alba leaf-based food modulates the gut microbiome and expression of genes related to obesity.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Apr 3;20(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-03961-9. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38570815 Free PMC article.
-
Mulberry leaf phenolics and fiber exert anti-obesity through the gut microbiota-host metabolism pathway.J Food Sci. 2021 Apr;86(4):1432-1447. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.15679. Epub 2021 Mar 24. J Food Sci. 2021. PMID: 33761137
-
Effect of flavonol glycoside in mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaf on glucose metabolism and oxidative stress in liver in diet-induced obese mice.J Sci Food Agric. 2010 Nov;90(14):2386-92. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4096. J Sci Food Agric. 2010. PMID: 20648552
-
Mulberry leaves and their potential effects against cardiometabolic risks: a review of chemical compositions, biological properties and clinical efficacy.Pharm Biol. 2018 Dec;56(1):109-118. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2018.1424210. Pharm Biol. 2018. PMID: 29347857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical potential and mechanistic insights of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves in managing type 2 diabetes mellitus: Focusing on gut microbiota, inflammation, and metabolism.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Apr 24;306:116143. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116143. Epub 2023 Jan 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36632855 Review.
Cited by
-
An olive oil-derived NAE mixture (Olaliamid®) improves liver and cardiovascular health, and decreases meta-inflammation in naturally obese dogs: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study.BMC Vet Res. 2025 Aug 6;21(1):505. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04946-y. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40764576 Free PMC article.
-
Isorhamnetin Regulates Programmed Death Ligand-1 Expression by Suppressing the EGFR-STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Canine Mammary Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 4;25(1):670. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010670. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203840 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Mulberry Leaf Powder on the Growth Performance, Lipid Metabolism Parameters, Immunity Indicators, and Gut Microbiota of Dogs.Metabolites. 2023 Aug 4;13(8):918. doi: 10.3390/metabo13080918. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37623861 Free PMC article.
-
Immune-mediated hematological disease in dogs is associated with alterations of the fecal microbiota: a pilot study.Anim Microbiome. 2023 Sep 29;5(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s42523-023-00268-2. Anim Microbiome. 2023. PMID: 37770990 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition on Risk of Relapse and Outcome to Eribulin or Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors in Metastatic Breast Cancer.JCO Precis Oncol. 2024 Dec;8:e2400274. doi: 10.1200/PO.24.00274. Epub 2024 Dec 6. JCO Precis Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39642326 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

