Identification of Agents That Ameliorate Hyperphosphatemia-Suppressed Myogenin Expression Involved in the Nrf2/p62 Pathway in C2C12 Skeletal Muscle Cells
- PMID: 36499650
- PMCID: PMC9736935
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232315324
Identification of Agents That Ameliorate Hyperphosphatemia-Suppressed Myogenin Expression Involved in the Nrf2/p62 Pathway in C2C12 Skeletal Muscle Cells
Abstract
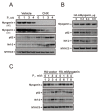
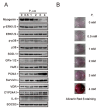
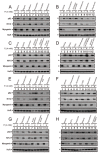
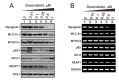
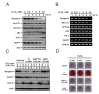
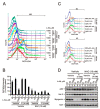
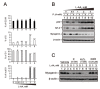
Hyperphosphatemia can occur as a result of reduced phosphate (Pi) excretion in cases of kidney dysfunction, which can induce muscle wasting and suppress myogenic differentiation. Higher Pi suppresses myogenic differentiation and promotes muscle atrophy through canonical (oxidative stress-mediated) and noncanonical (p62-mediated) activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) signaling. However, the crosstalk between myogenin and Nrf2/p62 and potential drug(s) for the regulation of myogenin expression needed to be addressed. In this study, we further identified that myogenin may negatively regulate Nrf2 and p62 protein levels in the mouse C2C12 muscle cell line. In the drug screening analysis, we identified N-acetylcysteine, metformin, phenformin, berberine, 4-chloro-3-ethylphenol, cilostazol, and cilomilast as ameliorating the induction of Nrf2 and p62 expression and reduction in myogenin expression that occur due to high Pi. We further elucidated that doxorubicin and hydrogen peroxide reduced the amount of myogenin protein mediated through the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1/Nrf2 pathway, differently from the mechanism of high Pi. The dual functional roles of L-ascorbic acid (L-AA) were found to be dependent on the working concentration, where concentrations below 1 mM L-AA reversed the effect of high Pi on myogenin and those above 1 mM L-AA had a similar effect of high Pi on myogenin when used alone. L-AA exacerbated the effect of hydrogen peroxide on myogenin protein and had no further effect of doxorubicin on myogenin protein. In summary, our results further our understanding of the crosstalk between myogenin and Nrf2, with the identification and verification of several potential drugs that can be applied in rescuing the decline of myogenin due to high Pi in muscle cells.
Keywords: L-ascorbic acid; hyperphosphatemia; myogenin; nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; p62.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

