Contribution of Asphalt Rubber Mixtures to Sustainable Pavements by Reducing Pavement Thickness
- PMID: 36500089
- PMCID: PMC9737376
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15238592
Contribution of Asphalt Rubber Mixtures to Sustainable Pavements by Reducing Pavement Thickness
Abstract
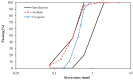
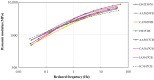
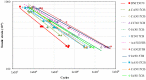
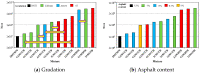
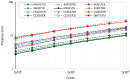
Asphalt rubber mixtures have been used as pavement surface layers due to their ability to prevent early degradation, and are considered a sustainable option. This study performed analysis comparing the fatigue resistance of asphalt rubber mixtures of different combinations of asphalt bases, crumb rubber, and gradation, in order to estimate the performance of asphalt rubber mixtures as pavement surface layers. The methodology was developed in a laboratory and involved asphalt rubber production by continuous and terminal blend systems with different crumb rubbers and asphalt base types. Asphalt rubber mixtures with varying gradations and an unmodified asphalt mixture as a reference were produced. The mechanical behavior as a dynamic modulus and with respect to fatigue resistance was evaluated using a four-point bending test. In order to verify each of the asphalt rubber mixtures' contribution as a surface layer, pavement structures were designed and their lifespans were compared. The findings showed that all asphalt rubber mixtures presented higher fatigue resistance than the reference. For pavement design, in comparison with the reference mixture, the thickness of the surface layer could be reduced by at least 50% while achieving the same life, proving its successful performance. This study demonstrated the effective contribution of crumb rubber from scrap tires as an asphalt modifier for producing sustainable mixtures with adequate fatigue performance.
Keywords: asphalt mixtures; asphalt rubber; cracking; performance; sustainable.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Brovelli C., Crispino M., Pais J.C., Pereira P. Assessment on fatigue resistance of modified asphalt concrete incorporating fibers and polymers. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014;26:554–558. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000837. - DOI
-
- Sengoz B., Agar E. Effect of asphalt film thickness on the moisture sensitivity characteristics of hot mix asphalt. Build. Environ. 2007;42:3621–3628. doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2006.10.006. - DOI
-
- Goldstein Market Intelligence (GMI) Global tire recycling industry report. London, United Kingdom. 2020. [(accessed on 6 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.goldsteinresearch.com/report/global-tire-recycling-industry-....
-
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Scrap Tires—Basic Information-United States. Washington, DC, USA: 2022. [(accessed on 6 November 2022)]. Available online: https://archive.epa.gov/epawaste/conserve/materials/tires/web/html/basic....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

