Top-Performance Transmission Gratings with Haloalkanes-Based Polymeric Composite Materials
- PMID: 36500134
- PMCID: PMC9738666
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15238638
Top-Performance Transmission Gratings with Haloalkanes-Based Polymeric Composite Materials
Abstract
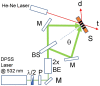
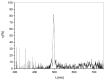
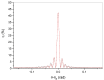
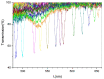
We report on highly transparent holographic phase transmission volume gratings recorded in the visible region at λ = 532 nm. The maximum measured diffraction efficiency is higher than 80% with a grating pitch of Λ≈ 300 nm and a refractive index modulation Δn ≈ 0.018. To obtain these results, we used a holographic mixture based on multi-reticulated acrylate and haloalkanes (1-bromo-butane and 1-bromo-hexane) and a synergic combination of camphore-quinone, which has a maximum absorbance at c.a. 470 nm, and R6G, here used as co-initiator, to efficiently initiate the photo-polymerization process. High transparent and high efficient holographic structures based on polymers can find applications in many research fields including integrated optics, sensors, high density data storage and security.
Keywords: acrylate; halo-alkanes; holographic gratings; polymers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Biswal T., BadJena S.K., Pradhan D. Synthesis of polymer composite materials and their biomedical applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2020;30:305–315. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.01.567. - DOI
-
- Tuttle M. Structural Analysis of Polymeric Composite Materials. 2nd ed. Chapman Hall/CRC Applied Env., Taylor & Francis; Oxfordshire, UK: 2012.
-
- Tsuchiya H., Asaki Y., Sinawang G., Asoh T.A., Osaki M., Park J., Ikemoto Y., Yamaguchi H., Harada A., Uyama H., et al. Cellulose Nanofiber Composite Polymeric Materials with Reversible and Movable Cross-links and Evaluation of their Mechanical Properties. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022;4:403–412. doi: 10.1021/acsapm.1c01332. - DOI
-
- Hsissou R., Seghiri R., Benzekri Z., Hilali M., Rafik M., Elharfi A. Polymer composite materials: A comprehensive review. Compos. Struct. 2021;262:113640. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.113640. - DOI
-
- Palermo G., Rippa M., Conti Y., Vestri A., Castagna R., Fusco G., Suffredini E., Zhou J., Zyss J., De Luca A., et al. Plasmonic Metasurfaces Based on Pyramidal Nanoholes for High-Efficiency SERS Biosensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2021;13:43715–43725. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c12525. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

