Lactobacillus paracasei HY7015 and Lycopus lucidus Turcz. Extract Promotes Human Dermal Papilla Cell Cytoprotective Effect and Hair Regrowth Rate in C57BL/6 Mice
- PMID: 36500327
- PMCID: PMC9738319
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27238235
Lactobacillus paracasei HY7015 and Lycopus lucidus Turcz. Extract Promotes Human Dermal Papilla Cell Cytoprotective Effect and Hair Regrowth Rate in C57BL/6 Mice
Abstract
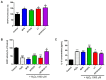
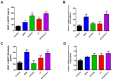
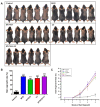
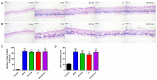
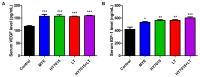
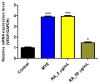
Hair loss is a disease that requires accurate diagnosis and type-specific medical treatment. Many hair loss treatments have some side effects, such as hormone-related effects, so there is a need for safe and effective hair loss treatment. In this study, we investigated the effects of Lactobacillus paracasei HY7015 (HY7015) and Lycopus lucidus Turcz. (LT) extract on hair regrowth and protection. In vitro experiments were conducted to assess the effects of HY7015 and/or LT extract on human follicle dermal papilla cells (HFDPC) of cytoprotective functions such as proliferations, antioxidants, anti-inflammatory, and growth factor expressions. In animal experiments, we investigated hair regrowth rate, hair follicle formation and secretion of growth factors in telogenic C57BL/6 mice. We confirmed the cytoprotective effects of HY7015 and LT through regulations of proliferation, SOD and IL-1β in HFDPC. In mouse experiments, oral administration of HY7015 and LT promoted hair regrowth as well as hair follicle maturation in the dermal skin of C57BL/6 mice, and upregulated VEGF and IGF-1 growth factor levels in mouse serum. In summary, our data demonstrate that ingestions of HY7015 and LT can promote hair regrowth by enhancing cytoprotective effects and expressions of growth factors.
Keywords: Lactobacillus paracasei; Lycopus lucidus Turcz.; cytoprotective effects; hair regrowth.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lactobacillus paracasei HY7015 Promotes Hair Growth in a Telogenic Mouse Model.J Med Food. 2021 Jul;24(7):741-748. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2020.4860. J Med Food. 2021. PMID: 34280032
-
Micro-Current Stimulation Has Potential Effects of Hair Growth-Promotion on Human Hair Follicle-Derived Papilla Cells and Animal Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 22;22(9):4361. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094361. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33921970 Free PMC article.
-
Hair-Growth-Promoting Effects of the Fish Collagen Peptide in Human Dermal Papilla Cells and C57BL/6 Mice Modulating Wnt/β-Catenin and BMP Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 7;23(19):11904. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911904. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233206 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of CXXC5 by a Competing Peptide Stimulates Hair Regrowth and Wound-Induced Hair Neogenesis.J Invest Dermatol. 2017 Nov;137(11):2260-2269. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2017.04.038. Epub 2017 Jun 6. J Invest Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28595998 Review.
-
Lagerstroemia indica extract regulates human hair dermal papilla cell growth and degeneration via modulation of β-catenin, Stat6, and TGF-β signaling pathway.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022 Jul;21(7):2763-2773. doi: 10.1111/jocd.15081. Epub 2022 Jun 9. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35596731 Review.
Cited by
-
Can Plant Extracts Help Prevent Hair Loss or Promote Hair Growth? A Review Comparing Their Therapeutic Efficacies, Phytochemical Components, and Modulatory Targets.Molecules. 2024 May 13;29(10):2288. doi: 10.3390/molecules29102288. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38792149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protection and Restoration of Damaged Hair via a Polyphenol Complex by Promoting Mechanical Strength, Antistatic, and Ultraviolet Protection Properties.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 Jul 9;8(3):296. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8030296. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37504184 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of probiotics in hair growth and dandruff control: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 16;10(9):e29539. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29539. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38698995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Horev L. Exogenous factors in hair disorders. Exog. Dermatol. 2004;3:237–245. doi: 10.1159/000091903. - DOI
-
- Arias-Santiago S., Arrabal-Polo M.A., Buendía-Eisman A., Arrabal-Martín M., Gutiérrez-Salmerón M.T., Girón-Prieto M.S., Jimenez-Pacheco A., Calonje J.E., Naranjo-Sintes R., Zuluaga-Gomez A., et al. Androgenetic alopecia as an early marker of benign prostatic hyperplasia. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012;66:401–408. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2010.12.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Farris P.K., Rogers N., McMichael A., Kogan S. A Novel Multi-Targeting Approach to Treating Hair Loss, Using Standardized Nutraceuticals. [(accessed on 1 November 2017)];J. Drugs Dermatol. 2017 16:141–148. Available online: https://jddonline.com/articles/a-novel-multi-targeting-approach-to-treat... - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

