High Throughput Fabrication of Flexible Top-Driven Sensing Probe
- PMID: 36501518
- PMCID: PMC9738077
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14235124
High Throughput Fabrication of Flexible Top-Driven Sensing Probe
Abstract
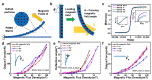
In this work, considering the current status of conservative and complicated traditional thrombosis treatment methods, a kind of flexible intelligent probe (FIP) with a top-driven sensing strategy is proposed to realize the expected function of thrombosis accurate localization in a liquid flow environment. After throughput fabrication, we find that the FIP has excellent electrical conductivity and mechanical properties. Notable, our FIP with the principle of piezo-resistive sensing has a quasi-linear sensitivity (approx. 0.325 L per minute) to flow sensing in the low flow velocity range (0-1 L per minute). Via the well-designed magnetically driven method, our FIP has a maximum deflection output force of 443.264 mN, a maximum deflection angle of 43°, and a maximum axial force of 54.176 mN. We demonstrate that the FIP is capable of completing the specified command actions relatively accurately and has a good response to real-time sensing feedback performance, which has broad application prospects in thrombus localization detection.
Keywords: flexible probe; smart materials; thrombus localization; top-driven sensing.
Conflict of interest statement
The co-authors all declare no competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Zhang X., Chen L., Lim K.H., Gonuguntla S., Lim K.W., Pranantyo D., Yong W., Yam W., Low Z., Teo W., et al. The Pathway to Intelligence: Using Stimuli-Responsive Materials as Building Blocks for Constructing Smart and Functional Systems. Adv. Mater. 2019;31:1804540. doi: 10.1002/adma.201804540. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang L., Qi H., Deng S., Cao L., Liu H., Hu S., Chen J. Design of superior electrostriction in BaTiO3-based lead-free relaxors via the formation of polarization nanoclusters. InfoMat. 2022;4:e12362.
-
- Sun Z., Yang L., Zhang D., Song W. High performance, flexible and renewable nano-biocomposite artificial muscle based on mesoporous cellulose/ionic liquid electrolyte membrane. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019;283:579–589. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.073. - DOI
-
- Sun Z., Du S., Li F., Yang L., Zhang D., Song W. High-performance cellulose based nanocomposite soft actuators with porous high-conductivity electrode doped by graphene-coated carbon nanosheet. Cellulose. 2018;25:5807–5819. doi: 10.1007/s10570-018-2000-3. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 51905085/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 52175266/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2018M630330/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project
- 2019T120245/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project
- 2572022CG08/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

