Formation and Characterization of Oregano Essential Oil Nanocapsules Applied onto Polyester Textile
- PMID: 36501585
- PMCID: PMC9736421
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14235188
Formation and Characterization of Oregano Essential Oil Nanocapsules Applied onto Polyester Textile
Abstract
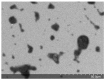
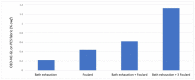
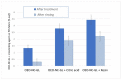
Oregano essential oil was encapsulated in poly-ϵ-caprolactone nanoparticles by a nanoprecipitation method using glycerin as a moisturizer. Nanocapsule characterization was performed by measuring the particle size, colloidal stability and encapsulation efficiency using dynamic light scattering, UV-Vis spectrophotometry and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The nanoparticles had a mean particle size of 235 nm with a monomodal distribution. In addition, a low polydispersity index was obtained, as well as a negative zeta potential of -36.3 mV and an encapsulation efficiency of 75.54%. Nanocapsules were applied to polyester textiles through bath exhaustion and foulard processing. Citric acid and a resin were applied as crosslinking agents to improve the nanocapsules' adhesion to the fabric. The adsorption, desorption, moisture content and essential oil extraction were evaluated to determine the affinity between the nanocapsules and the polyester. The adsorption was higher when the citric acid and the resin were applied. When standard oregano nanocapsules were used, almost all of the impregnated nanoparticles were removed when washed with water. The moisture content was evaluated for treated and non-treated textiles. There was a significant increase in the moisture content of the treated polyester compared to the non-treated polyester, which indicates that the polyester hydrophilicity increased with an important absorption of the essential oil nanocapsules; this can improve fabric comfort and probably promote antibacterial properties.
Keywords: glycerol; nanoprecipitation; oregano essential oil; polyester; polymeric nanocapsules.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fraj A., Jaâfar F., Marti M., Coderch L., Ladhari N. A comparative study of oregano (Origanum vulgare L.) essential oil-based polycaprolactone nanocapsules/microspheres: Preparation, physicochemical characterization, and storage stability. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019;140:111669. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111669. - DOI
-
- Pecarski D., Knezevic-Jugovic Z., Dimitrijevic-Brankovic S., Mihajilovski K., Jankovic S. Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial activity of chitosan microparticles with thyme essential oil. Chem. Ind. 2014;68:721–729. doi: 10.2298/HEMIND140415048P. - DOI
-
- Agu A.B.S., Benablo P.J.L., Mesias V.S.D., Penaloza D.P., Jr. Synthesis and Characterization of a Chitosan-Based Citric Acid-Crosslinked Encapsulant System. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2019;64:4610–4612. doi: 10.4067/S0717-97072019000404610. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

