Malware Detection in Internet of Things (IoT) Devices Using Deep Learning
- PMID: 36502007
- PMCID: PMC9735444
- DOI: 10.3390/s22239305
Malware Detection in Internet of Things (IoT) Devices Using Deep Learning
Abstract
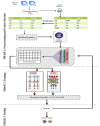
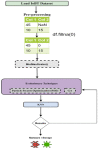
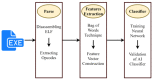
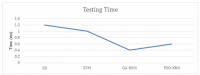
Internet of Things (IoT) devices usage is increasing exponentially with the spread of the internet. With the increasing capacity of data on IoT devices, these devices are becoming venerable to malware attacks; therefore, malware detection becomes an important issue in IoT devices. An effective, reliable, and time-efficient mechanism is required for the identification of sophisticated malware. Researchers have proposed multiple methods for malware detection in recent years, however, accurate detection remains a challenge. We propose a deep learning-based ensemble classification method for the detection of malware in IoT devices. It uses a three steps approach; in the first step, data is preprocessed using scaling, normalization, and de-noising, whereas in the second step, features are selected and one hot encoding is applied followed by the ensemble classifier based on CNN and LSTM outputs for detection of malware. We have compared results with the state-of-the-art methods and our proposed method outperforms the existing methods on standard datasets with an average accuracy of 99.5%.
Keywords: CNN; Internet of Things; LSTM; malware detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Novel Detection and Multi-Classification Approach for IoT-Malware Using Random Forest Voting of Fine-Tuning Convolutional Neural Networks.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 6;22(11):4302. doi: 10.3390/s22114302. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35684922 Free PMC article.
-
Biserial Miyaguchi-Preneel Blockchain-Based Ruzicka-Indexed Deep Perceptive Learning for Malware Detection in IoMT.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Oct 27;21(21):7119. doi: 10.3390/s21217119. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34770424 Free PMC article.
-
IoT malware detection architecture using a novel channel boosted and squeezed CNN.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 15;12(1):15498. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18936-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36109570 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Study of Anomaly Detection Schemes in IoT Networks Using Machine Learning Algorithms.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Dec 13;21(24):8320. doi: 10.3390/s21248320. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34960414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of Botnet Attack Detection in SDN-Enabled IoT Using Machine Learning.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;22(24):9837. doi: 10.3390/s22249837. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560204 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of the Authentication Techniques for Internet of Things Devices in Smart Cities: Opportunities, Challenges, and Future Directions.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Mar 7;25(6):1649. doi: 10.3390/s25061649. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40292695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
OEDL: an optimized ensemble deep learning method for the prediction of acute ischemic stroke prognoses using union features.Front Neurol. 2023 Jun 21;14:1158555. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1158555. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37416306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mendez D.M., Papapanagiotou I., Yang B. Internet of things: Survey on security and privacy. arXiv. 20171707.01879
-
- Tama B.A., Rhee K.H. An integration of pso-based feature selection and random forest for anomaly detection in iot network. MATEC Web Conf. 2018;159:01053. doi: 10.1051/matecconf/201815901053. - DOI
-
- Naeem H., Ullah F., Naeem M.R., Khalid S., Vasan D., Jabbar S., Saeed S. Malware detection in industrial internet of things based on hybrid image visualization and deep learning model. Ad Hoc Netw. 2020;105:102154. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2020.102154. - DOI
-
- Moti Z., Hashemi S., Karimipour H., Dehghantanha A., Jahromi A.N., Abdi L., Alavi F. Generative adversarial network to detect unseen internet of things malware. Ad Hoc Netw. 2021;122:102591. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2021.102591. - DOI
-
- Humayun M., Jhanjhi N., Alsayat A., Ponnusamy V. Internet of things and ransomware: Evolution, mitigation and prevention. Egypt. Inform. J. 2021;22:105–117. doi: 10.1016/j.eij.2020.05.003. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

