Highly Sensitive and Selective Formaldehyde Gas Sensors Based on Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Nitrogen-Doped Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
- PMID: 36502032
- PMCID: PMC9739274
- DOI: 10.3390/s22239329
Highly Sensitive and Selective Formaldehyde Gas Sensors Based on Polyvinylpyrrolidone/Nitrogen-Doped Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
Abstract
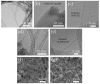
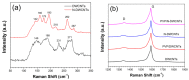
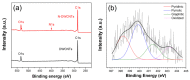
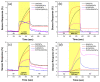
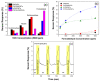
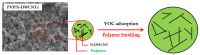
A highly sensitive and selective formaldehyde sensor was successfully fabricated using hybrid materials of nitrogen-doped double-walled carbon nanotubes (N-DWCNTs) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). Double-walled carbon nanotubes (DWCNTs) and N-DWCNTs were produced by high-vacuum chemical vapor deposition using ethanol and benzylamine, respectively. Purified DWCNTs and N-DWCNTs were dropped separately onto the sensing substrate. PVP was then dropped onto pre-dropped DWCNT and N-DWCNTs (hereafter referred to as PVP/DWCNTs and PVP/N-DWCNTs, respectively). As-fabricated sensors were used to find 1,2-dichloroethane, dichloromethane, formaldehyde and toluene vapors in parts per million (ppm) at room temperature for detection measurement. The sensor response of N-DWCNTs, PVP/DWCNTs and PVP/N-DWCNTs sensors show a high response to formaldehyde but a low response to 1,2-dichloroethane, dichloromethane and toluene. Remarkably, PVP/N-DWCNTs sensors respond sensitively and selectively towards formaldehyde vapor, which is 15 times higher than when using DWCNTs sensors. This improvement could be attributed to the synergistic effect of the polymer swelling and nitrogen-sites in the N-DWCNTs. The limit of detection (LOD) of PVP/N-DWCNTs was 15 ppm, which is 34-fold higher than when using DWCNTs with a LOD of 506 ppm. This study demonstrated the high sensitivity and selectivity for formaldehyde-sensing applications of high-performance PVP/N-DWCNTs hybrid materials.
Keywords: formaldehyde; gas sensors; nitrogen-doped double-walled carbon nanotubes; polyvinylpyrrolidone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Beasley R.K., Hoffmann C.E., Rueppel M.L., Worley J.W. Sampling of formaldehyde in air with coated solid sorbent and determination by high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1980;52:1110–1114. doi: 10.1021/ac50057a026. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

