Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation Architecture Supported by a Distributed Data Acquisition System
- PMID: 36502234
- PMCID: PMC9740827
- DOI: 10.3390/s22239532
Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation Architecture Supported by a Distributed Data Acquisition System
Abstract
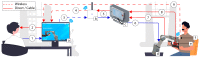
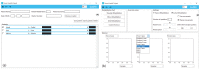
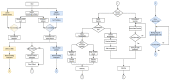
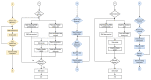
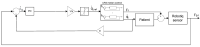
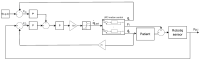
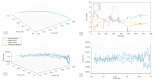
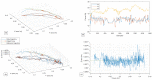
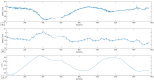
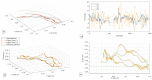
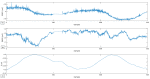
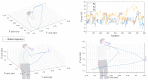
Rehabilitation robotics aims to facilitate the rehabilitation procedure for patients and physical therapists. This field has a relatively long history dating back to the 1990s; however, their implementation and the standardisation of their application in the medical field does not follow the same pace, mainly due to their complexity of reproduction and the need for their approval by the authorities. This paper aims to describe architecture that can be applied to industrial robots and promote their application in healthcare ecosystems. The control of the robotic arm is performed using the software called SmartHealth, offering a 2 Degree of Autonomy (DOA). Data are gathered through electromyography (EMG) and force sensors at a frequency of 45 Hz. It also proves the capabilities of such small robots in performing such medical procedures. Four exercises focused on shoulder rehabilitation (passive, restricted active-assisted, free active-assisted and Activities of Daily Living (ADL)) were carried out and confirmed the viability of the proposed architecture and the potential of small robots (i.e., the UR3) in rehabilitation procedure accomplishment. This robot can perform the majority of the default exercises in addition to ADLs but, nevertheless, their limits were also uncovered, mainly due to their limited Range of Motion (ROM) and cost.
Keywords: UR3; data acquisition; electromyography sensor; graphical user interface; rehabilitation robotics; upper limb.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chellal A.A., Lima J., Fernandes F.P., Gonçalves J., Pacheco M.F., Monteiro F.C. International Conference on Optimization, Learning Algorithms and Applications. Springer; Bragança, Portugal: 2021. Overview of robotic based system for rehabilitation and healthcare; pp. 515–530.
-
- Li M., Zhang J., Zuo G., Feng G., Zhang X. Assist-as-needed control strategy of bilateral upper limb rehabilitation robot based on GMM. Machines. 2022;10:76. doi: 10.3390/machines10020076. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- UIDB/05757/2020 and UIDP/05757/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- LA/P/0007/2021/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- SFRH/BD/08598/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000045/SmartHealth - Inteligência Artificial para Cuidados de Saúde Personalizados ao Longo da Vida
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

