Effects of COVID-19 Pandemic on Voluntary Medical Male Circumcision Services for HIV Prevention, Sub-Saharan Africa, 2020
- PMID: 36502454
- PMCID: PMC9745243
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2813.212455
Effects of COVID-19 Pandemic on Voluntary Medical Male Circumcision Services for HIV Prevention, Sub-Saharan Africa, 2020
Abstract
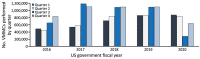
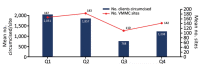
Beginning in March 2020, to reduce COVID-19 transmission, the US President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief supporting voluntary medical male circumcision (VMMC) services was delayed in 15 sub-Saharan African countries. We reviewed performance indicators to compare the number of VMMCs performed in 2020 with those performed in previous years. In all countries, the annual number of VMMCs performed decreased 32.5% (from 3,898,960 in 2019 to 2,631,951 in 2020). That reduction is largely attributed to national and local COVID-19 mitigation measures instituted by ministries of health. Overall, 66.7% of the VMMC global annual target was met in 2020, compared with 102.0% in 2019. Countries were not uniformly affected; South Africa achieved only 30.7% of its annual target in 2020, but Rwanda achieved 123.0%. Continued disruption to the VMMC program may lead to reduced circumcision coverage and potentially increased HIV-susceptible populations. Strategies for modifying VMMC services provide lessons for adapting healthcare systems during a global pandemic.
Keywords: 2019 novel coronavirus disease; COVID-19; HIV prevention; HIV/AIDS; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus disease; impacts of COVID-19; respiratory infections; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; sub-Saharan Africa; viruses; voluntary medical male circumcision; zoonoses.
Figures
References
-
- Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. On the fast-track to end AIDS [cited 2021 Jun 25]. https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/20151027_UNAIDS_P...
-
- World Health Organization, Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS. New data on male circumcision and HIV prevention: policy and programme implications [cited 2022 Jun 27]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241595988
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

