KCa-Related Neurological Disorders: Phenotypic Spectrum and Therapeutic Indications
- PMID: 36503451
- PMCID: PMC10472807
- DOI: 10.2174/1570159X21666221208091805
KCa-Related Neurological Disorders: Phenotypic Spectrum and Therapeutic Indications
Abstract
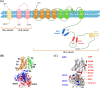
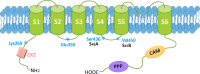
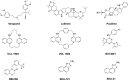
Although potassium channelopathies have been linked to a wide range of neurological conditions, the underlying pathogenic mechanism is not always clear, and a systematic summary of clinical manifestation is absent. Several neurological disorders have been associated with alterations of calcium-activated potassium channels (KCa channels), such as loss- or gain-of-function mutations, post-transcriptional modification, etc. Here, we outlined the current understanding of the molecular and cellular properties of three subtypes of KCa channels, including big conductance KCa channels (BK), small conductance KCa channels (SK), and the intermediate conductance KCa channels (IK). Next, we comprehensively reviewed the loss- or gain-of-function mutations of each KCa channel and described the corresponding mutation sites in specific diseases to broaden the phenotypic-genotypic spectrum of KCa-related neurological disorders. Moreover, we reviewed the current pharmaceutical strategies targeting KCa channels in KCa-related neurological disorders to provide new directions for drug discovery in anti-seizure medication.
Keywords: Potassium channels; action potential; channelopathies; epilepsy; modulators; pharmacology.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures
References
-
- Gutman G.A., Chandy K.G., Grissmer S., Lazdunski M., Mckinnon D., Pardo L.A., Robertson G.A., Rudy B., Sanguinetti M.C., Stühmer W., Wang X. International Union of Pharmacology. LIII. Nomenclature and molecular relationships of voltage-gated potassium channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005;57(4):473–508. doi: 10.1124/pr.57.4.10. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barcia G., Fleming M.R., Deligniere A., Gazula V.R., Brown M.R., Langouet M., Chen H., Kronengold J., Abhyankar A., Cilio R., Nitschke P., Kaminska A., Boddaert N., Casanova J.L., Desguerre I., Munnich A., Dulac O., Kaczmarek L.K., Colleaux L., Nabbout R. De novo gain-of-function KCNT1 channel mutations cause malignant migrating partial seizures of infancy. Nat. Genet. 2012;44(11):1255–1259. doi: 10.1038/ng.2441. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

