A low-cost and open-source solution to automate imaging and analysis of cyst nematode infection assays for Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 36503537
- PMCID: PMC9743603
- DOI: 10.1186/s13007-022-00963-2
A low-cost and open-source solution to automate imaging and analysis of cyst nematode infection assays for Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
Background: Cyst nematodes are one of the major groups of plant-parasitic nematode, responsible for considerable crop losses worldwide. Improving genetic resources, and therefore resistant cultivars, is an ongoing focus of many pest management strategies. One of the major bottlenecks in identifying the plant genes that impact the infection, and thus the yield, is phenotyping. The current available screening method is slow, has unidimensional quantification of infection limiting the range of scorable parameters, and does not account for phenotypic variation of the host. The ever-evolving field of computer vision may be the solution for both the above-mentioned issues. To utilise these tools, a specialised imaging platform is required to take consistent images of nematode infection in quick succession.
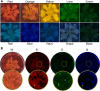
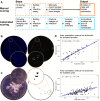
Results: Here, we describe an open-source, easy to adopt, imaging hardware and trait analysis software method based on a pre-existing nematode infection screening method in axenic culture. A cost-effective, easy-to-build and -use, 3D-printed imaging device was developed to acquire images of the root system of Arabidopsis thaliana infected with the cyst nematode Heterodera schachtii, replacing costly microscopy equipment. Coupling the output of this device to simple analysis scripts allowed the measurement of some key traits such as nematode number and size from collected images, in a semi-automated manner. Additionally, we used this combined solution to quantify an additional trait, root area before infection, and showed both the confounding relationship of this trait on nematode infection and a method to account for it.
Conclusion: Taken together, this manuscript provides a low-cost and open-source method for nematode phenotyping that includes the biologically relevant nematode size as a scorable parameter, and a method to account for phenotypic variation of the host. Together these tools highlight great potential in aiding our understanding of nematode parasitism.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are not aware of competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Sasser JN. A world perspective on nematology: the role of the society. Vistas Nematol. 1987;7–14.
-
- Atkinson HJ, Urwin PE, Hansen E, McPherson MJ. Designs for engineered resistance to root-parasitic nematodes. Trends Biotechnol. 1995;13:369–374. doi: 10.1016/S0167-7799(00)88983-0. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

