Enhancing cancer differentiation with synthetic MRI examinations via generative models: a systematic review
- PMID: 36503979
- PMCID: PMC9742072
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-022-01315-3
Enhancing cancer differentiation with synthetic MRI examinations via generative models: a systematic review
Abstract
Contemporary deep learning-based decision systems are well-known for requiring high-volume datasets in order to produce generalized, reliable, and high-performing models. However, the collection of such datasets is challenging, requiring time-consuming processes involving also expert clinicians with limited time. In addition, data collection often raises ethical and legal issues and depends on costly and invasive procedures. Deep generative models such as generative adversarial networks and variational autoencoders can capture the underlying distribution of the examined data, allowing them to create new and unique instances of samples. This study aims to shed light on generative data augmentation techniques and corresponding best practices. Through in-depth investigation, we underline the limitations and potential methodology pitfalls from critical standpoint and aim to promote open science research by identifying publicly available open-source repositories and datasets.
Keywords: Data augmentation; Generative adversarial networks; Magnetic resonance imaging; Synthetic medical images; Variational autoencoders.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
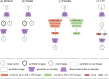

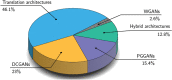
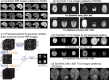
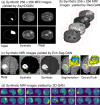
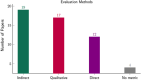
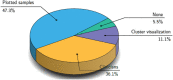
References
-
- Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2017) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: communications of the ACM. NIPS’12 vol 60, pp 84–90 Curran Associates Inc., Red Hook, NY, USA 10.1145/3065386
-
- Jia Deng, Wei Dong, Socher, R. Li-Jia Li, Kai Li, Li Fei-Fei (2009) ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. 10.1109/cvprw.2009.5206848
-
- Ian Goodfellow YB, Courville A (2016) Deep learning deep learning 29:1–73
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

