Effects of Aloe Vera in the Treatment of Oral Ulcers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials
- PMID: 36504087
- PMCID: PMC11640788
- DOI: 10.3290/j.ohpd.b3666483
Effects of Aloe Vera in the Treatment of Oral Ulcers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials
Abstract
Purpose: To analyse the effects of aloe vera on the treatment of oral ulcers.
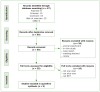
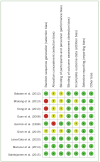
Materials and methods: Relevant studies were identified from PubMed, Embase, ClinicalTrials.gov, SinoMed, Web of Science and Cochrane Library. Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) involving aloe vera (AV) in the treatment of oral ulcers were included. The data were extracted and pooled for meta-analysis to compare the clinical outcomes of patients with oral ulcers in terms of treatment effect, the size of ulcers, Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) for pain, and therapy duration. The standardised mean differences (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were determined for the main outcomes, heterogeneity was analysed using the I2 test, and the studies' risk of bias was evaluating using the Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool.
Results: The study included 9 trials with a total of 847 participants. Seven trials were included in the meta-analysis. The results indicated no statistically significant differences in pain scores as assessed by the VAS (I2 = 95%, p = 0.89; SMD: -0.12, 95% CI: -1.84, 1.60) and size of ulcers (I2 = 88%, p = 0.60; SMD: -0.29, 95% CI: -1.39, 0.81). Clinical efficacy of the aloe vera group was better compared to control group (I2 = 89%, p = 0.007; RR: 2.25, 95% CI: 1.25, 4.06). Therapy duration was statistically significantly lower following AV gel application in two of the studies (I2 = 0%, p < 0.001; SMD: -1.32, 95% CI: -1.84, -0.79). Considering the results in a systematic manner, AV accelerated tissue epithelialisation and the wound-healing process.
Conclusion: Compared with other interventions, aloe vera has a better therapeutic effect and shorter healing time. It is comparable with other interventions in relieving pain and reducing ulcer size, but it has higher safety and almost no side effects.
Keywords: Aloe vera; clinical therapeutic effect assessment; meta-analysis; randomised controlled trials (RCTs); treatment of oral ulcers.
Figures




References
-
- Al-Maweri SA, Ashraf S, Lingam AS, Alqutaibi A, Abdulrab S, Alaizari N, et al. Aloe vera in treatment of oral submucous fibrosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Oral Pathol Med. 2019;48:99–107. - PubMed
-
- Al-Maweri SA, Nassani MZ, Alaizari N, Kalakonda B, Al-Shamiri HM, Alhajj MN, et al. Efficacy of aloe vera mouthwash versus chlorhexidine on plaque and gingivitis: A systematic review. Int J Dent Hyg. 2020;18:44–51. - PubMed
-
- Bhalang K, Thunyakitpisal P, Rungsirisatean N. Acemannan, a polysaccharide extracted from Aloe vera, is effective in the treatment of oral aphthous ulceration. J Altern Complement Med. 2013;19:429–434. - PubMed
-
- Choonhakarn C, Busaracome P, Sripanidkulchai B. The efficacy of aloe vera gel in the treatment of oral lichen planus: a randomized controlled trial. Br J Dermatol. 2008;158:573–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

