Oxytocin and Hypotension During Dilation and Evacuation Procedures at 18-24 Weeks Gestation
- PMID: 36504503
- PMCID: PMC9727702
Oxytocin and Hypotension During Dilation and Evacuation Procedures at 18-24 Weeks Gestation
Abstract
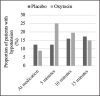
Oxytocin is a neurohormone that is routinely administered to patients during dilation and evacuation procedures (D&E) to control bleeding despite minimal evidence in support of this common practice. In this study, the authors sought to evaluate patients with hypotension after receiving oxytocin during D&E procedures. The secondary data from a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial involving 112 patients who underwent a D&E at 18-24 weeks gestation and prophylactically received an intravenous bolus of either 30 units of oxytocin in 500 mL of normal saline or 500 mL of saline alone at the start of the procedure were analyzed. Anesthesia providers measured blood pressure before, at the time of, and after study medication administration in 5-minute increments until the end of the procedure. No differences in demographic characteristics or mean blood pressure between the 2 groups were observed. The proportion of hypotensive patients was not statistically different at 5 minutes following fluid bolus (oxytocin 25% versus placebo 13%, P=.09). The proportion of hypotensive patients was similar by 10 minutes (oxytocin 20% versus placebo 16%, P=.62). A sample size of 112 provided the ability to detect a 23% difference in the proportion of patients who experienced hypotension (2-sided 95% CI, power of 80%). These findings suggest that oxytocin may have a transient hypotensive effect.
Keywords: blood pressure; hypotensive; oxytocin.
©Copyright 2022 by University Health Partners of Hawai‘i (UHP Hawai‘i).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Prophylactic Oxytocin on Bleeding Outcomes in Women Undergoing Dilation and Evacuation: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Mar;133(3):484-491. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003104. Obstet Gynecol. 2019. PMID: 30741801 Clinical Trial.
-
Intramuscular oxytocin versus intravenous oxytocin to prevent postpartum haemorrhage at vaginal delivery (LabOR trial): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2017 Nov 15;18(1):541. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-2269-9. Trials. 2017. PMID: 29141679 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association between prophylactic oxytocin use during dilation and evacuation and estimated blood loss.Contraception. 2017 Jul;96(1):19-24. doi: 10.1016/j.contraception.2017.04.003. Epub 2017 May 5. Contraception. 2017. PMID: 28483553
-
Effect of partograph use on outcomes for women in spontaneous labour at term and their babies.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 6;8(8):CD005461. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005461.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30080256 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous oxytocin dosing regimens for postpartum hemorrhage prevention following cesarean delivery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Sep;225(3):250.e1-250.e38. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.04.258. Epub 2021 May 4. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33957113
References
-
- Whitehouse K, Tschann M, Soon R, et al. Effects of prophylactic oxytocin on bleeding outcomes in women undergoing dilation and evacuation: A randomized controlled trial [published correction appears in Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Jun;133(6):1287-1288] Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133((3)):484–49. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003104. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources