Effect of naturally-occurring mutations on the stability and function of cancer-associated NQO1: Comparison of experiments and computation
- PMID: 36504709
- PMCID: PMC9730889
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1063620
Effect of naturally-occurring mutations on the stability and function of cancer-associated NQO1: Comparison of experiments and computation
Abstract
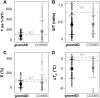
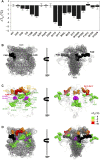
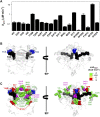
Recent advances in DNA sequencing technologies are revealing a large individual variability of the human genome. Our capacity to establish genotype-phenotype correlations in such large-scale is, however, limited. This task is particularly challenging due to the multifunctional nature of many proteins. Here we describe an extensive analysis of the stability and function of naturally-occurring variants (found in the COSMIC and gnomAD databases) of the cancer-associated human NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1). First, we performed in silico saturation mutagenesis studies (>5,000 substitutions) aimed to identify regions in NQO1 important for stability and function. We then experimentally characterized twenty-two naturally-occurring variants in terms of protein levels during bacterial expression, solubility, thermal stability, and coenzyme binding. These studies showed a good overall correlation between experimental analysis and computational predictions; also the magnitude of the effects of the substitutions are similarly distributed in variants from the COSMIC and gnomAD databases. Outliers in these experimental-computational genotype-phenotype correlations remain, and we discuss these on the grounds and limitations of our approaches. Our work represents a further step to characterize the mutational landscape of NQO1 in the human genome and may help to improve high-throughput in silico tools for genotype-phenotype correlations in this multifunctional protein associated with disease.
Keywords: computational prediction; genotype-phenotype correlations; protein function; protein stability; sequence conservation.
Copyright © 2022 Pacheco-Garcia, Cagiada, Tienne-Matos, Salido, Lindorff-Larsen and L. Pey.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

