P53 maintains gallid alpha herpesvirus 1 replication by direct regulation of nucleotide metabolism and ATP synthesis through its target genes
- PMID: 36504811
- PMCID: PMC9729838
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1044141
P53 maintains gallid alpha herpesvirus 1 replication by direct regulation of nucleotide metabolism and ATP synthesis through its target genes
Abstract
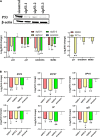
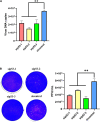
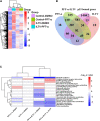
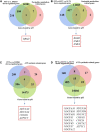
P53, a well-known tumor suppressor, has been confirmed to regulate the infection of various viruses, including chicken viruses. Our previous study observed antiviral effect of p53 inhibitor Pifithrin-α (PFT-α) on the infection of avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV), one of the major avian viruses economically significant to the poultry industry globally. However, the potential link between this antiviral effect of PFT-α and p53 remains unclear. Using chicken LMH cell line which is permissive for ILTV infection as model, we explore the effects of p53 on ILTV replication and its underlying molecular mechanism based on genome-wide transcriptome analysis of genes with p53 binding sites. The putative p53 target genes were validated by ChIP-qPCR and RT-qPCR. Results demonstrated that, consistent with the effects of PFT-α on ILTV replication we previously reported, knockdown of p53 repressed viral gene transcription and the genome replication of ILTV effectively. The production of infectious virions was also suppressed significantly by p53 knockdown. Further bioinformatic analysis of genes with p53 binding sites revealed extensive repression of these putative p53 target genes enriched in the metabolic processes, especially nucleotide metabolism and ATP synthesis, upon p53 repression by PFT-α in ILTV infected LMH cells. Among these genes, eighteen were involved in nucleotide metabolism and ATP synthesis. Then eight of the 18 genes were selected randomly for validations, all of which were successfully identified as p53 target genes. Our findings shed light on the mechanisms through which p53 controls ILTV infection, meanwhile expand our knowledge of chicken p53 target genes.
Keywords: P53; PFT-α; alphaherpesviruses; virus replication; virus-host interactions.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Chen, Zhang, Cui, Liu, Li, Liu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the Effects of Host p53 and Fos on Gallid Alpha Herpesvirus 1 Replication.Genes (Basel). 2023 Aug 12;14(8):1615. doi: 10.3390/genes14081615. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628666 Free PMC article.
-
PFT-α inhibits gallid alpha herpesvirus 1 replication by repressing host nucleotide metabolism and ATP synthesis.Vet Microbiol. 2022 Jun;269:109435. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2022.109435. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Vet Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35462119
-
Integrative RNA-seq and ChIP-seq analysis unveils metabolic regulation as a conserved antiviral mechanism of chicken p53.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Aug 6;12(8):e0030924. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00309-24. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38888361 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular biology of avian infectious laryngotracheitis virus.Vet Res. 2007 Mar-Apr;38(2):261-79. doi: 10.1051/vetres:200657. Epub 2007 Feb 13. Vet Res. 2007. PMID: 17296156 Review.
-
The route of inoculation dictates the replication patterns of the infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV) pathogenic strain and chicken embryo origin (CEO) vaccine.Avian Pathol. 2017 Dec;46(6):585-593. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2017.1331029. Epub 2017 Jun 19. Avian Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28532159 Review.
Cited by
-
Review of respiratory syndromes in poultry: pathogens, prevention, and control measures.Vet Res. 2025 May 17;56(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s13567-025-01506-y. Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40382667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-Regulation Mechanism of Host p53 and Fos in Transcriptional Activation of ILTV Immediate-Early Gene ICP4.Microorganisms. 2024 Oct 16;12(10):2069. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12102069. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39458378 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analyses of host-virus interactions during in vitro infection with wild-type and glycoprotein g-deficient (ΔgG) strains of ILTV in primary and continuous cell cultures.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 11;19(10):e0311874. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311874. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39392810 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Effects of Host p53 and Fos on Gallid Alpha Herpesvirus 1 Replication.Genes (Basel). 2023 Aug 12;14(8):1615. doi: 10.3390/genes14081615. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37628666 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

