Clinical efficacy and safety of flunarizine tablets combined with betahistine hydrochloride tablets in patients with vertebrobasilar insufficiency vertigo
- PMID: 36505311
- PMCID: PMC9730052
Clinical efficacy and safety of flunarizine tablets combined with betahistine hydrochloride tablets in patients with vertebrobasilar insufficiency vertigo
Abstract
Objective: To explore the clinical efficacy and safety of betahistine hydrochloride tablets in patients with vertebrobasilar insufficiency vertigo (VBIV).
Methods: A total of 133 patients with vertigo caused by vertebrobasilar insufficiency treated in The First People's Hospital of Shangqiu City from March 2019 to August 2021 were selected and analyzed retrospectively. Among them, 63 patients treated with flunarizine tablets were seen as the control group (CG), and 70 with flunarizine tablets combined with betastine hydrochloride tablets were considered as the observation group (OG). The treatment efficacy and adverse reactions were compared, and the vertigo symptom score, quality of life and vertebrobasilar artery hemodynamics were observed before and after treatment.
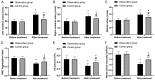
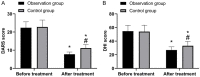
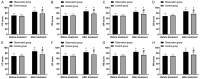
Results: The effective rate in the OG was higher than that of the CG (P<0.05), but there was no obvious difference in adverse reactions (P>0.05). Compared with the CG, the arterial hemodynamics and cerebral blood perfusion as well as SF-36 score were higher, while the scores of dizziness assessment rating scale (DARS) and dizziness handicap inventory (DHI) scale were lower in the OG (all P<0.05).
Conclusion: Betahistine hydrochloride can effectively improve arterial hemodynamics and cerebral blood flow perfusion in vertebrobasilar insufficiency patients and enhance the clinical efficacy with high safety profile, which is worthy of wide application.
Keywords: Betahistine hydrochloride tablets; clinical efficacy; flunarizine tablets; vertebrobasilar insufficiency vertigo.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
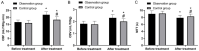
Similar articles
-
Effects of flunarizine combined with ginkgo leaf extract and dipyridamole injection on hemorheology in elderly patients with vertigo.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Jan-Feb;40(3Part-II):337-341. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.3.8456. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38356833 Free PMC article.
-
[The efficacy of topiramate and flunarizine hydrochloride for prophylactic treatment of vestibular migraine].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021 Sep;35(9):784-787;795. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.09.004. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34628829 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Double-blind, randomized, multicenter study comparing the effect of betahistine and flunarizine on the dizziness handicap in patients with recurrent vestibular vertigo.Acta Otolaryngol. 2003 Jun;123(5):588-93. doi: 10.1080/00016480310001475. Acta Otolaryngol. 2003. PMID: 12875580 Clinical Trial.
-
Flunarizine in the treatment of vertigo.J Laryngol Otol. 1983 Aug;97(8):697-704. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100094858. J Laryngol Otol. 1983. PMID: 6350513 Review.
-
[Betahistine in vestibular disorders: current concepts and perspectives].Vestn Otorinolaringol. 2021;86(2):73-81. doi: 10.17116/otorino20218602173. Vestn Otorinolaringol. 2021. PMID: 33929156 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Effects of flunarizine combined with ginkgo leaf extract and dipyridamole injection on hemorheology in elderly patients with vertigo.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Jan-Feb;40(3Part-II):337-341. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.3.8456. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38356833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han SM, Lee HS, Chae HS, Seo YJ. Usefulness of vertebrobasilar artery radiological finding as a predictive and prognostic factor for sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2021;48:823–829. - PubMed
-
- Thomas L, Treleaven J. Should we abandon positional testing for vertebrobasilar insufficiency? Musculoskelet Sci Pract. 2020;46:102095. - PubMed
-
- Rennert RC, Steinberg JA, Strickland BA, Ravina K, Bakhsheshian J, Fredrickson V, Pannell JS, Khalessi AA, Russin JJ. Extracranial-to-intracranial bypass for refractory vertebrobasilar insufficiency. World Neurosurg. 2019;126:552–559. - PubMed
-
- Guo Z, Su Z, Wang Z, Luo X, Lai R. The effect of Chinese herbal medicine Banxia Baizhu Tianma Decoction for the treatment of vertebrobasilar insufficiency vertigo: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement Ther Med. 2017;31:27–38. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
