Patterns of essential trace elements (Cr, Mn, Ni, and Se) in Saudi patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 36505325
- PMCID: PMC9730081
Patterns of essential trace elements (Cr, Mn, Ni, and Se) in Saudi patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Objectives: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) outcomes were observed to be influenced by circulating trace elements' status. The differences and correlations between serum levels of chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), nickel (Ni), and selenium (Se) in Saudi patients with and without T2DM as well as those with prediabetes (pre-DM) were examined in this retrospective cross-sectional study.
Methods: Anthropometrics and fasting blood samples were collected from 119 patients with T2DM (aged 41-64 years), 95 non-T2DM (aged 27-55 years), and 80 with pre-DM (aged 35-57 years). An inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer was used to measure trace minerals in the blood.
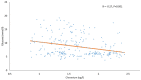
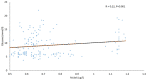
Results: T2DM patients had significantly lower Mn serum concentrations than controls. There was no difference in Cr and Ni levels between groups. Serum Mn and Ni levels were lower in pre-DM subjects than controls. Serum Se concentrations were higher in pre-DM and T2DM patients than controls. In T2DM patients, serum Cr and Mn levels were inversely correlated with glucose, while Ni and Se levels were positively correlated with glucose in the T2DM group.
Conclusions: Because of their roles in glucose metabolism, impaired trace element status may also play a role in T2DM pathogenesis. Appropriate dietary control and mineral supplementation are recommended.
Keywords: Saudi; Type 2 diabetes; trace elements.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Patterns and Associations of Essential Trace Elements (Cu, Fe and Zn) in Saudi Adults with Varying Levels of Glycemia.Metabolites. 2021 May 6;11(5):297. doi: 10.3390/metabo11050297. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34066324 Free PMC article.
-
Trace and toxic element patterns in nonsmoker patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, impaired glucose tolerance, and fasting glucose.Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2009 Jan;29(1):35-40. doi: 10.4103/0973-3930.50713. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2009. PMID: 20062562 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-sectional study: Relationship between serum trace elements and hypertension.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2022 Jan;69:126893. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2021.126893. Epub 2021 Nov 10. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 34798511
-
Effectiveness and safety of selenium supplementation for type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials.J Hum Nutr Diet. 2019 Oct;32(5):635-645. doi: 10.1111/jhn.12670. Epub 2019 May 30. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2019. PMID: 31148299
-
Association of Selenium Intake and Selenium Concentrations with Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Adults: A Narrative Review.Metabolites. 2023 Jun 19;13(6):767. doi: 10.3390/metabo13060767. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37367924 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Evaluation of Selected Trace Elements in Blood, Serum and Blood Cells of Type 2 Diabetes Patients with and without Renal Disorder.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 4;16(17):2989. doi: 10.3390/nu16172989. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39275304 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the application of ionomics in metabolic diseases.Front Nutr. 2023 Jan 16;9:1111933. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1111933. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36726817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between nickel exposure and diabetes risk: an updated meta-analysis of observational studies.Front Public Health. 2024 Nov 5;12:1463880. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1463880. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39564359 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Serum Concentrations of (Certain) Metals and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 6;13(23):7443. doi: 10.3390/jcm13237443. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39685901 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A, Chan JCN, Mbanya JC, Pavkov ME, Ramachandaran A, Wild SH, James S, Herman WH, Zhang P, Bommer C, Kuo S, Boyko EJ, Magliano DJ. IDF diabetes atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
