Effect of rapid rehabilitation nursing on inflammation and liver function after laparoscopic radical resection of primary liver cancer
- PMID: 36505328
- PMCID: PMC9730087
Effect of rapid rehabilitation nursing on inflammation and liver function after laparoscopic radical resection of primary liver cancer
Abstract
Objective: To explore the effect of rapid rehabilitation nursing on inflammation and liver function in patients with primary liver cancer (PLC) after laparoscopic radical resection.
Methods: A total of 124 PLC patients who underwent laparoscopic radical surgery in the Zhuji People's Hospital of Zhejiang Province from April 2019 to July 2021 were enrolled in this retrospective study. Among them, 65 patients who received rapid rehabilitation nursing were assigned into the observation group (OG), and the other 59 with routine nursing were considered to be the control group (CG). The pain before operation (T0), 3 days after operation (T1) and 7 days after operation (T2) was evaluated by visual analogue scale (VAS). The perioperative related indexes and nursing satisfaction were compared. The levels of liver function indexes alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin (TBIL) and inflammatory factors C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were measured before operation, 1 day and 7 days after operation. Finally, the incidence of postoperative complications was counted, the 6-month survival rate of both groups of patients was compared.
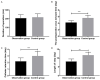
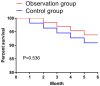
Results: There was no obvious difference in VAS scores between the two groups at T0 (P>0.050), but the VAS scores at T1 and T2 in the OG were lower than those in the CG (P<0.001). There was no marked difference in the total operation time. Compared with the CG, the time to first exhaust, catheter indwelling and hospitalization in the OG were shorter (P<0.001) and the nursing satisfaction rate was higher (P<0.05). There was no obvious difference in ALT, AST and TBIL on the 1st day after operation (P>0.05); however, on the 7th day after operation, ALT and AST were lower while TBIL was higher in the OG (all P<0.05). There was no marked difference in CRP, IL-6 and TNF-α between the two groups on postoperative day 1 (P>0.05), but the levels were lower in the OG than those in the CG on postoperative day 7 (all P<0.05), and the total incidence of adverse reactions in the OG was lower (P<0.05). There was no statistical difference in the postoperative survival rate between both groups of patients (P>0.05). Age, number of lesions, tumor size, Child-Pugh grade, AST, TBIL, CRP, IL-6, TNF-α were associated with the survival rate of patients.
Conclusion: Rapid rehabilitation nursing can effectively reduce adverse reactions after laparoscopic radical resection of PLC. Thus, it has a high application value in future clinical treatment.
Keywords: Laparoscopic radical resection of primary liver cancer; inflammation; liver function; rapid rehabilitation nursing.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
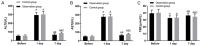
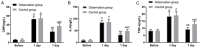
Similar articles
-
The impact of laparoscopic radical gastrectomy on the inflammatory response and immune function of patients with gastric cancer.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2024 Jun 5;70(6):92-96. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2024.70.6.15. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2024. PMID: 38836675
-
Personalized nursing improves physical condition and life quality of patients undergoing interventional therapy for liver cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Dec 15;13(12):14220-14228. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 35035768 Free PMC article.
-
High-quality nursing can reduce the incidence of adverse events in esophageal cancer patients after operation in the intensive care unit and improve postoperative rehabilitation.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Oct 15;13(10):11851-11859. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34786114 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy of laparoscopic radical hepatectomy and laparotomy for hepatocellular carcinoma and factors of postoperative recurrence.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 22;13:1116984. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1116984. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37035189 Free PMC article.
-
Application Effect of Laparoscopic Myomectomy and Comprehensive Rehabilitation Nursing on Patients with Uterine Fibroids.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Sep 22;2022:4018803. doi: 10.1155/2022/4018803. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 36238468 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enhanced recovery after surgery speeds up healing for hip fracture patients.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Jul 15;16(7):3231-3239. doi: 10.62347/AEVL7890. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39114676 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of rapid rehabilitation surgery nursing on patients undergoing radical thyroidectomy.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Dec 15;15(12):7013-7022. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 38186990 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Linggui Zhugan decoction on microwave ablation outcomes and recurrence in liver cancer.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Feb 15;17(2):101177. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i2.101177. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39958537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fan X, Gu L, Lv S, Zhang M, Zhuang L, Zhang Y, Chen P. Suppression of the transforming growth factor-beta signaling pathway produces a synergistic effect of combination therapy with programmed death receptor 1 blockade and radiofrequency ablation against hepatic carcinoma in mice. Bioengineered. 2022;13:9046–9058. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang S, Xiong Z, Liu Y, Leng Y, Deng H, Shen D, Meng X, Liu T. Efficacy and safety of acupuncture and moxibustion combined with the external application of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of primary liver cancer: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021;100:e27659. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pla-Alemany S, Romero JA, Santabarbara JM, Aliaga R, Maceira AM, Moratal D. Automatic multi-atlas liver segmentation and Couinaud classification from CT volumes. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021;2021:2826–2829. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
