Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel bioactive thalidomide analogs as anticancer immunomodulatory agents
- PMID: 36505721
- PMCID: PMC9680624
- DOI: 10.1039/d2ra06188k
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel bioactive thalidomide analogs as anticancer immunomodulatory agents
Abstract
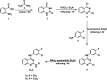
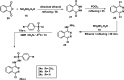
Cancer is still a dangerous disease with a high mortality rate all over the world. In our attempt to develop potential anticancer candidates, new quinazoline and phthalazine based compounds were designed and synthesized. The new derivatives were built in line with the pharmacophoric features of thalidomide. The new derivatives as well as thalidomide were examined against three cancer cell lines, namely: hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG-2), breast cancer (MCF-7) and prostate cancer (PC3). Then the effects on the expression levels of caspase-8, VEGF, NF-κB P65, and TNF-α in HepG-2 cells were evaluated. The biological data revealed the high importance of phthalazine based compounds (24a-c), which were far better than thalidomide with regard to the antiproliferative activity. 24b showed IC50 of 2.51, 5.80 and 4.11 μg mL-1 compared to 11.26, 14.58, and 16.87 μg mL-1 for thalidomide against the three cell lines respectively. 24b raised caspase-8 level by about 7 folds, compared to 8 folds reported for thalidomide. Also, VEGF level in HepG-2 cells treated with 24b was 185.3 pg mL-1, compared to 432.5 pg mL-1 in control cells. Furthermore, the immunomodulatory properties were proven to 24b, which reduced TNF-α level by approximately half. At the same time, NF-κB P65 level in HepG-2 cells treated with 24b was 76.5 pg mL-1 compared to 278.1 and 110.5 pg mL-1 measured for control cells and thalidomide treated HepG-2 cells respectively. Moreover, an in vitro viability study against Vero non-cancerous cell line was investigated and the results reflected a high safety profile of all tested compounds. This work suggests 24b as a promising lead compound for development of new immunomodulatory anticancer agents.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of New Potential Unusual Modified Anticancer Immunomodulators for Possible Non-Teratogenic Quinazoline-Based Thalidomide Analogs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 4;24(15):12416. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512416. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569792 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis, anticancer evaluation, and in silico ADMET analysis of novel thalidomide analogs as promising immunomodulatory agents.RSC Adv. 2023 Apr 3;13(16):10488-10502. doi: 10.1039/d3ra00066d. eCollection 2023 Apr 3. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37021105 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of New Immunomodulatory Anticancer Thalidomide Analogs: Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and In Silico Studies.Chem Biodivers. 2025 Mar;22(3):e202401768. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202401768. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 39540225
-
Immunomodulatory properties of thalidomide analogs: pomalidomide and lenalidomide, experimental and therapeutic applications.Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 2011 Sep;5(3):192-6. doi: 10.2174/187221411797265890. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21913886 Review.
-
Targeting the interplay between MMP-2, CA II and VEGFR-2 via new sulfonamide-tethered isomeric triazole hybrids; Microwave-assisted synthesis, computational studies and evaluation.Bioorg Chem. 2022 Jul;124:105816. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.105816. Epub 2022 Apr 16. Bioorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 35489270 Review.
Cited by
-
Design, synthesis, anti-proliferative evaluation, docking, and MD simulation studies of new thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidines targeting VEGFR-2.RSC Adv. 2023 Aug 4;13(33):23365-23385. doi: 10.1039/d3ra03128d. eCollection 2023 Jul 26. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37545598 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting VEGFR-2 in breast cancer: synthesis and in silico and in vitro characterization of quinoxaline-based inhibitors.RSC Adv. 2025 Apr 22;15(17):12896-12916. doi: 10.1039/d5ra00526d. eCollection 2025 Apr 22. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40271404 Free PMC article.
-
Quinazolinone based broad-spectrum antiviral molecules: design, synthesis, in silico studies and biological evaluation.Mol Divers. 2025 Jun 13. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11237-z. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 40512342
-
Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of New Potential Unusual Modified Anticancer Immunomodulators for Possible Non-Teratogenic Quinazoline-Based Thalidomide Analogs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 4;24(15):12416. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512416. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569792 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Flavone Derivative Displaying a 4'-Aminophenoxy Moiety as Potential Selective Anticancer Agent in NSCLC Tumor Cells.Molecules. 2023 Apr 5;28(7):3239. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073239. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37050002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdallah A. E. Mabrouk R. R. Elnagar M. R. Farrag A. M. Kalaba M. H. Sharaf M. H. El-Fakharany E. M. Bakhotmah D. A. Elkaeed E. B. Al Ward M. M. S. New Series of VEGFR-2 Inhibitors and Apoptosis Enhancers: Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Drug Des., Dev. Ther. 2022;16:587. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S344750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Simon J. A. Szankasi P. Nguyen D. K. Ludlow C. Dunstan H. M. Roberts C. J. Jensen E. L. Hartwell L. H. Friend S. H. Differential toxicities of anticancer agents among DNA repair and checkpoint mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cancer Res. 2000;60(2):328–333. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

