The efficacy and safety of Apatinib in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective trial
- PMID: 36505785
- PMCID: PMC9727187
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1030798
The efficacy and safety of Apatinib in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective trial
Abstract
Background: As a potent inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway, Apatinib has been used in antitumor treatment for some time. The study aimed to research the therapeutic effects and toxicity of Apatinib in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 128 NSCLC patients treated with Apatinib in Qilu Hospital of Shandong University. Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) criteria was adopted to evaluate the treatment effect, and Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 4.0 was conducted to determine the Adverse Events (AEs). Cox proportional hazard model and Kaplan-Meier function were applied to evaluate the progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
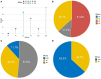
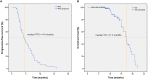
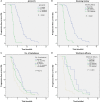
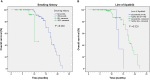
Results: Among 128 NSCLC patients, partial response (PR) were observed in 15 patients, stable disease (SD) in 66 patients and progressive disease (PD) in 47 patients. The objective response rate (ORR) and disease control rate (DCR) accounted for 11.7% and 63.3% respectively. The median PFS (mPFS) and median OS (mOS) were 4.4 months and 17.2 months. Common side effects of Apatinib were hypertension (n=48), proteinuria (n=35), and hand-foot syndrome (HFS) (n=30), all of the side effects were controllable. No significant difference was observed in efficacy and AEs between the higher dose group (Apatinib>500mg/d) and the lower dose group (Apatinib=500mg/d).
Conclusions: The study suggested that Apatinib with a lower dose (=500mg/d) has good efficacy and safety in the treatment of advanced NSCLC after first-line chemotherapy.
Keywords: advanced non-small cell lung cancer; anti-angiogenesis; apatinib; safety; survival.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Huang, Yang, Song, Jia, Chen and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and Safety of Apatinib Treatment for Advanced Cholangiocarcinoma After Failed Gemcitabine-Based Chemotherapy: An Open-Label Phase II Prospective Study.Front Oncol. 2021 May 3;11:659217. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.659217. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34012920 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy, safety and predictive indicators of apatinib after multilines treatment in advanced nonsquamous nonsmall cell lung cancer: Apatinib treatment in nonsquamous NSCLC.Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2018 Dec;14(6):446-452. doi: 10.1111/ajco.12870. Epub 2018 Mar 24. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29573236
-
Efficacy and safety of apatinib as second or later-line therapy in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: a prospective, exploratory, single-arm, multi-center clinical trial.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 May;11(5):832-844. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-313. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35693282 Free PMC article.
-
The safety of apatinib for the treatment of gastric cancer.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2018 Nov;17(11):1145-1150. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2018.1535592. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2018. PMID: 30324820 Review.
-
Apatinib in recurrent anaplastic meningioma: a retrospective case series and systematic literature review.Cancer Biol Ther. 2020 Jul 2;21(7):583-589. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2020.1740053. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32212907 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Apatinib monotherapy for early non-small cell lung cancer: a case report.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024 Oct 1;19(1):557. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-03088-w. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 39354591 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

