Prognostic value and immune infiltration of the gasdermin family in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 36505798
- PMCID: PMC9732578
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1043862
Prognostic value and immune infiltration of the gasdermin family in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: The GSDM family includes six members, GSDMA, GSDMB, GSDMC, GSDMD, GSDME (DFNA5), and PJVK (Pejvakin, DFNB59), which can induce pyroptosis, thereby regulating the tumorigenesis of various cancers. However, the clinical characteristics and role of the GSDM family in LUAD are not well understood.
Methods: In this study, several important bioinformatics databases were used to integrate the analysis of the expression, prognostic value, and immune infiltration of GSDMs in LUAD. These databases include UALCAN, DiseaseMeth, GEPIA, THPA, cBioPortal, TIMER, WebGestalt, STRING database, and Cytoscape.
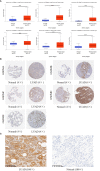
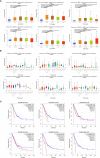
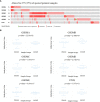
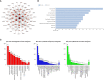
Results: The findings from the UALCAN database revealed that the expression of all six GSDMs based on the tumor stage in LUAD was increased (particularly GSDMD). Our IHC results verified it. Additionally, the DiseaseMeth database showed that the methylation levels of GSDMA, GSDMB, GSDMC, and GSDMD were decreased. The expression of six GSDMs was related to shorter overall survival in patients with LUAD, according to the GEPIA database. The cBioPortal database was further used to explore the alteration rate and correlated genes in LUAD. Subsequently, these genes were subjected to functional enrichment and protein-protein interaction network analyses. We identified that the GSDM family regulate several signaling pathways, including immune-associated signaling pathways. According to tumor-infiltrating immune cell analysis from the TIMER database, GSDM family members are associated with the infiltration of important immune cells and their signature markers.
Conclusions: GSDM family may be prognostic markers and novel strategies for the treatment of LUAD.
Keywords: GSDM family; biomarker; immune infiltration; lung adenocarcinoma; methylation; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Peng, Duan, Li, Wang, Han, Huang, Yu, Ou and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
GSDMB: A novel, independent prognostic marker and potential new therapeutic target in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2024 Jan 5;27(2):85. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14219. eCollection 2024 Feb. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38249806 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment the value of Pyroptosis-Associated Gasdermin family genes in hepatocellular carcinoma: A Multi-Omics Comprehensive Analysis.J Cancer. 2024 Feb 12;15(7):1966-1982. doi: 10.7150/jca.88887. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38434972 Free PMC article.
-
A pan-cancer analysis of the expression of gasdermin genes in tumors and their relationship with the immune microenvironment.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Sep;10(9):4125-4147. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-1635. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116710 Free PMC article.
-
Gasdermins: pore-forming activities and beyond.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020 May 26;52(5):467-474. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmaa016. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020. PMID: 32294153 Review.
-
Pyroptosis, inflammasome, and gasdermins in tumor immunity.Innate Immun. 2023 Jan;29(1-2):3-13. doi: 10.1177/17534259221143216. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Innate Immun. 2023. PMID: 36632024 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of gasdermin family proteins in cancers (Review).Int J Oncol. 2023 Sep;63(3):100. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5548. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Int J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37477150 Free PMC article.
-
TBK1 Reprograms Metabolism in Breast Cancer: An Integrated Omics Approach.J Proteome Res. 2025 Jan 3;24(1):121-133. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00530. Epub 2024 Dec 13. J Proteome Res. 2025. PMID: 39670797 Free PMC article.
-
Pyroptosis, gasdermins and allergic diseases.Allergy. 2024 Sep;79(9):2380-2395. doi: 10.1111/all.16236. Epub 2024 Jul 14. Allergy. 2024. PMID: 39003568 Review.
-
C6 and KLRG2 are pyroptosis subtype-related prognostic biomarkers and correlated with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in lung adenocarcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 22;14(1):24861. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75650-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39438534 Free PMC article.
-
Gasdermins: a dual role in pyroptosis and tumor immunity.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 18;15:1322468. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1322468. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38304430 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tomášková H, Horáček J, Šlachtová H, Šplíchalová A, Riedlová P, Dalecká A, et al. . Analysis of histopathological findings of lung carcinoma in Czech black coal miners in association with coal workers' pneumoconiosis. Int J Environ Res Public Health (2022) 19(2):710. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19020710 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

