Which lymph node dissection template is optimal for radical cystectomy? A systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis
- PMID: 36505883
- PMCID: PMC9732561
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.986150
Which lymph node dissection template is optimal for radical cystectomy? A systematic review and Bayesian network meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to determine the optimal pelvic lymph node dissection (PLND) template for radical cystectomy (RC).
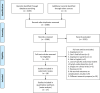
Methods: A systematic search was conducted using the PubMed, Embase and Cochrane Library database in December 2021. Articles comparing recurrence-free survival (RFS), disease-specific survival (DSS), overall survival (OS), and postoperative complications among patients undergoing limited PLND (lPLND), standard PLND (sPLND), extended PLND (ePLND), or super-extended PLND (sePLND) were included. A Bayesian approach was used for network meta-analysis.
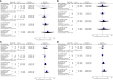
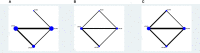
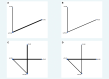
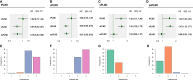
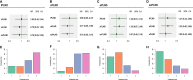
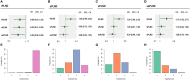
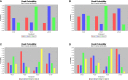
Results: We included 18 studies in this systematic review, and 17 studies met our criteria for network meta-analysis. We performed meta-analyses and network meta-analyses to investigate the associations between four PLND templates and the RFS, DSS, OS, or postoperative complications. We found that the ePLND group and the sePLND group were associated with better RFS than the sPLND group (Hazard Ratio [HR]: 0.65, 95% Credible Interval [CrI]: 0.56 to 0.78) (HR: 0.67, 95% CrI: 0.56 to 0.83) and the lPLND group (HR: 0.67, 95% CrI: 0.50 to 0.91) (HR: 0.70, 95% CrI: 0.49 to 0.99). For RFS, Analysis of the treatment ranking revealed that ePLND had the highest probabilities to be the best template. There was no significant difference between the four templates in DSS, however, analysis of the treatment ranking indicated that sePLND had the highest probabilities to be the best template. And We found that the sePLND group and the ePLND group were associated with better OS than lPLND (HR: 0.58, 95% CrI: 0.36 to 0.95) (HR: 0.63, 95% CrI: 0.41 to 0.94). For OS, analysis of the treatment ranking revealed that sePLND had the highest probabilities to be the best template. The results of meta-analyses and network meta-analyses showed that postoperative complications rates did not differ significantly between any two templates.
Conclusion: Patients undergoing sePLND and ePLND had better RFS but not better DSS or OS than those undergoing lPLND or sPLND templates, however, RFS did not differ between patients undergoing sePLND or ePLND. Considering that sePLND involves longer operation time, higher risk, and greater degree of difficulty than ePLND, and performing sePLND may not result in better prognosis, so it seems that there is no need for seLPND. We think that ePLND might be the optimal PLND template for RC.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42022318475.
Keywords: Bayesian analysis; bladder cancer; complications; pelvic lymph node dissection; prognosis.
Copyright © 2022 Qi, Zhong, Jiang, Zhou, Lv, Li, Shi and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of the extent of lymph node dissection on survival outcomes in clinically lymph node-positive bladder cancer.BJU Int. 2024 Mar;133(3):341-350. doi: 10.1111/bju.16210. Epub 2023 Nov 15. BJU Int. 2024. PMID: 37904652
-
Balancing risk and benefit of extended pelvic lymph node dissection in patients undergoing radical cystectomy.World J Urol. 2016 Jan;34(1):41-8. doi: 10.1007/s00345-015-1734-x. Epub 2015 Nov 30. World J Urol. 2016. PMID: 26621208
-
Extended versus non-extended lymphadenectomy during radical cystectomy for patients with bladder cancer: a meta-analysis of the effect on long-term and short-term outcomes.World J Surg Oncol. 2019 Dec 21;17(1):225. doi: 10.1186/s12957-019-1759-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31864368 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative analysis of perioperative complications and biochemical recurrence between standard and extended pelvic lymph node dissection in prostate cancer patients undergoing radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2024 Mar 1;110(3):1735-1743. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000997. Int J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38052016 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of perioperative complications for extended vs standard pelvic lymph node dissection in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer: a meta-analysis.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2022 Apr 15;10(2):73-81. eCollection 2022. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2022. PMID: 35528467 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sentinel lymph node dissection during radical cystectomy for bladder adenocarcinoma following gastrocystoplasty.Urol Case Rep. 2025 Apr 9;60:103036. doi: 10.1016/j.eucr.2025.103036. eCollection 2025 May. Urol Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40276711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- IARC . Estimated number of new cases in 2020, worldwide, both sexes, all ages (2020). Available at: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/900-world-fact-she....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

