HLA-BAT1 alters migration, invasion and pro-inflammatory cytokines in prostate cancer
- PMID: 36505884
- PMCID: PMC9727259
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.969396
HLA-BAT1 alters migration, invasion and pro-inflammatory cytokines in prostate cancer
Abstract
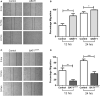
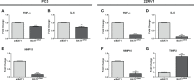
Prostate cancer (PCa) accounts for more than 1 in 5 diagnoses and is the second cause of cancer-related deaths in men. Although PCa may be successfully treated, patients may undergo cancer recurrence and there is a need for new biomarkers to improve the prediction of prostate cancer recurrence and improve treatment. Our laboratory demonstrated that HLA-B-associated transcript 1 (BAT1) was differentially expressed in patients with high Gleason scores when compared to low Gleason scores. BAT1 is an anti-inflammatory gene but its role in PCa has not been identified. The objective of this study is to understand the role of BAT1 in prostate cancer. In vitro studies showed that BAT1 down-regulation increased cell migration and invasion. In contrast, BAT1 overexpression decreased cell migration and invasion. RT-PCR analysis showed differential expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6) and cell adhesion and migration genes (MMP10, MMP13, and TIMPs) in BAT1 overexpressed cells when compared to BAT1 siRNA cells. Our in vivo studies demonstrated up-regulation of TNF-α, IL-6, and MMP10 in tumors developed from transfected BAT1 shRNA cells when compared to tumors developed from BAT1 cDNA cells. These findings indicate that BAT1 down-regulation modulates TNF-α and IL-6 expression which may lead to the secretion of MMP-10 and inhibition of TIMP2.
Keywords: animal models; cytokines; inflammation; invasion; migration; prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2022 García-Vargas, Roque-Reyes, Arroyo-Villegas, Santiago-Negron, Sánchez-Vázquez, Rivera-Torres, Reyes-Meléndez, Cardona-Berdecía, García-Maldonado, Víquez and Martínez-Ferrer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Screening for prostate cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jan 31;2013(1):CD004720. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004720.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 23440794 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

