Comprehensive multi-omics analysis of the m7G in pan-cancer from the perspective of predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine
- PMID: 36505892
- PMCID: PMC9727047
- DOI: 10.1007/s13167-022-00305-1
Comprehensive multi-omics analysis of the m7G in pan-cancer from the perspective of predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine
Abstract
Background: The N7-methylguanosine modification (m7G) of the 5' cap structure in the mRNA plays a crucial role in gene expression. However, the relation between m7G and tumor immune remains unclear. Hence, we intended to perform a pan-cancer analysis of m7G which can help explore the underlying mechanism and contribute to predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine (PPPM / 3PM).
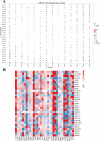
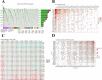
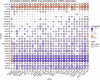
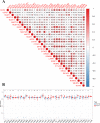
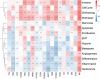
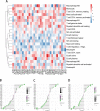
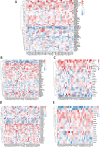
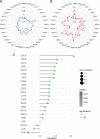
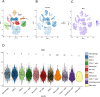
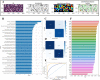
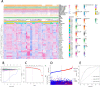
Methods: The gene expression, genetic variation, clinical information, methylation, and digital pathological section from 33 cancer types were downloaded from the TCGA database. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) was used to validate the expression of the m7G regulator genes (m7RGs) hub-gene. The m7G score was calculated by single-sample gene-set enrichment analysis. The association of m7RGs with copy number variation, clinical features, immune-related genes, TMB, MSI, and tumor immune dysfunction and exclusion (TIDE) was comprehensively assessed. CellProfiler was used to extract pathological section characteristics. XGBoost and random forest were used to construct the m7G score prediction model. Single-cell transcriptome sequencing (scRNA-seq) was used to assess the activation state of the m7G in the tumor microenvironment.
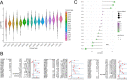
Results: The m7RGs were highly expressed in tumors and most of the m7RGs are risk factors for prognosis. Moreover, the cellular pathway enrichment analysis suggested that m7G score was closely associated with invasion, cell cycle, DNA damage, and repair. In several cancers, m7G score was significantly negatively correlated with MSI and TMB and positively correlated with TIDE, suggesting an ICB marker potential. XGBoost-based pathomics model accurately predicts m7G scores with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.97. Analysis of scRNA-seq suggests that m7G differs significantly among cells of the tumor microenvironment. IHC confirmed high expression of EIF4E in breast cancer. The m7G prognostic model can accurately assess the prognosis of tumor patients with an AUC of 0.81, which was publicly hosted at https://pan-cancer-m7g.shinyapps.io/Panca-m7g/.
Conclusion: The current study explored for the first time the m7G in pan-cancer and identified m7G as an innovative marker in predicting clinical outcomes and immunotherapeutic efficacy, with the potential for deeper integration with PPPM. Combining m7G within the framework of PPPM will provide a unique opportunity for clinical intelligence and new approaches.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13167-022-00305-1.
Keywords: Protein-protein interaction analysis; Immune regulation; Immunotherapy; Machine learning; Multi-omics; N7-methylguanosine modification; Pan-cancer analysis; Predictive preventive personalized medicine (PPPM / 3PM); Single-cell transcriptome sequencing; Tumor microenvironment.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to European Association for Predictive, Preventive and Personalised Medicine (EPMA) 2022, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Doebele RC, et al. An oncogenic NTRK fusion in a patient with soft-tissue sarcoma with response to the tropomyosin-related kinase inhibitor LOXO-101. Cancer Discov. 2015;5:1049–1057. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-15-0443. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

