Satisfaction with comprehensive emergency obstetric and newborn care services and associated factors among clients in University of Gondar Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 36505972
- PMCID: PMC9729994
- DOI: 10.1177/20503121221141558
Satisfaction with comprehensive emergency obstetric and newborn care services and associated factors among clients in University of Gondar Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Objective: Emergency obstetric and newborn care services treat 70-80% of maternal deaths. This study aimed to assess satisfaction with comprehensive emergency obstetric and newborn care (CEmONC) services and associated factors among clients in the University of Gondar Specialized Hospital.
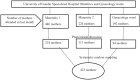
Methods: Institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted on 404 participants using a systematic random sampling method. The study was conducted from March 5 to May 5, 2020, using interviewer-administered structured questionnaires. Binary logistic regression was used to find the association between independent variables and client satisfaction. The level of statistical significance was declared at a p value less than 0.05.
Results: The overall clients' satisfaction with CEmONC services was 65.1% (95% confidence interval (CI): 60.9-69.8). Clients' satisfaction was affected by women who had antenatal care (ANC) of three visits (adjusted odds ratio (AOR): 6.5; 95%, CI: 2.04-20.8), women waited less than 15 min (AOR: 4.15, 95% CI: 1.9-9.06), mothers stayed ⩽1 day (AOR: 0.28, 95% CI: 0.09-0.9) and 2-3 days (AOR: 0.98, 95% CI: 0.1-0.69), obtaining a welcoming environment (AOR: 4.6, 95% CI: 2.15-9.88), and getting providers explanation of examinations (AOR: 3.3, 95% CI: 1.97-5.52).
Conclusion: The observed clients' satisfaction with CEmONC services was suboptimal. Having ANC of three visits, waiting less than 15 min, duration of stay, obtaining a welcoming environment, and an explanation of providers' examination were the identified factors of client's satisfaction. Therefore, hospital managers and health professionals should work on the identified factors to increase the client's satisfaction with these services.
Keywords: Client satisfaction; University of Gondar Specialized Hospital; comprehensive emergency obstetric and newborn care services.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the implementation fidelity of comprehensive emergency obstetric and newborn care at University of Gondar comprehensive specialized hospital, Northwest Ethiopia: a mixed-method evaluation.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Aug 12;24(1):532. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06725-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 39134928 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive emergency management of obstetric and newborn care program implementation at University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia, 2021: an evaluation study.Reprod Health. 2023 May 19;20(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12978-023-01623-x. Reprod Health. 2023. PMID: 37208688 Free PMC article.
-
Mental healthcare services satisfaction and its associated factors among patients with mental disorders on follow-up in the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia.Front Psychiatry. 2023 May 30;14:1081968. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1081968. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37324812 Free PMC article.
-
Women's satisfaction with comprehensive abortion care services and associated factors in central Gondar zone public primary hospitals, northwest Ethiopia, 2023.Front Reprod Health. 2024 Oct 1;6:1400359. doi: 10.3389/frph.2024.1400359. eCollection 2024. Front Reprod Health. 2024. PMID: 39411054 Free PMC article.
-
Enrollment and clients' satisfaction with a community-based health insurance scheme: a community-based survey in Northwest Ethiopia.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Jan 13;24(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-10570-7. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 38218770 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Maternal satisfaction with emergency obstetric and newborn care services in Ethiopia and the associated factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Womens Health (Lond). 2023 Jan-Dec;19:17455057231183854. doi: 10.1177/17455057231183854. Womens Health (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37377356 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the implementation fidelity of comprehensive emergency obstetric and newborn care at University of Gondar comprehensive specialized hospital, Northwest Ethiopia: a mixed-method evaluation.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 Aug 12;24(1):532. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06725-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 39134928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey P, Lobis S, Maine D, et al.. Monitoring emergency obstetric care: a handbook. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2009.
-
- WHO. Maternal mortality. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2014.
-
- Central Statistical Agency. Ethiopian demographic and health survey 2016. Addis Ababa: The DHS Program, 2017.
-
- WHO. Trends in maternal mortality. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources