Differentiation of pluripotent stem cells for modeling human skin development and potential applications
- PMID: 36506084
- PMCID: PMC9728031
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1030339
Differentiation of pluripotent stem cells for modeling human skin development and potential applications
Abstract
The skin of mammals is a multilayered and multicellular tissue that forms an environmental barrier with key functions in protection, regulation, and sensation. While animal models have long served to study the basic functions of the skin in vivo, new insights are expected from in vitro models of human skin development. Human pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) have proven to be invaluable tools for studying human development in vitro. To understand the mechanisms regulating human skin homeostasis and injury repair at the molecular level, recent efforts aim to differentiate PSCs towards skin epidermal keratinocytes, dermal fibroblasts, and skin appendages such as hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Here, we present an overview of the literature describing strategies for human PSC differentiation towards the components of skin, with a particular focus on keratinocytes. We highlight fundamental advances in the field employing patient-derived human induced PSCs (iPSCs) and skin organoid generation. Importantly, PSCs allow researchers to model inherited skin diseases in the search for potential treatments. Skin differentiation from human PSCs holds the potential to clarify human skin biology.
Keywords: 3D skin models; epidermal differentiation; human induced pluripotent stem cells; iPSCs; keratinocyte; skin inherited diseases; skin organoids.
Copyright © 2022 Oceguera-Yanez, Avila-Robinson and Woltjen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
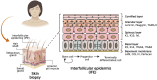
Figures

References
-
- Bakkers J., Hild M., Kramer C., Furutani-Seiki M., Hammerschmidt M. (2002). Zebrafish DeltaNp63 is a direct target of Bmp signaling and encodes a transcriptional repressor blocking neural specification in the ventral ectoderm. Dev. Cell. 2 (5), 617–627. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

