Application of Mn x Fe1- x Fe2O4 (x = 0-1) Nanoparticles in Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia: Correlation with Cation Distribution and Magnetostructural Properties
- PMID: 36506172
- PMCID: PMC9730757
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c05651
Application of Mn x Fe1- x Fe2O4 (x = 0-1) Nanoparticles in Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia: Correlation with Cation Distribution and Magnetostructural Properties
Abstract
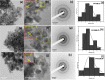
Optimization of manganese-substituted iron oxide nanoferrites having the composition Mn x Fe1-x Fe2O4 (x = 0-1) has been achieved by the chemical co-precipitation method. The crystallite size and phase purity were analyzed from X-ray diffraction. With increases in Mn2+ concentration, the crystallite size varies from 5.78 to 9.94 nm. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) analysis depicted particle sizes ranging from 10 ± 0.2 to 13 ± 0.2 nm with increasing Mn2+ substitution. The magnetization (M s) value varies significantly with increasing Mn2+ substitution. The variation in the magnetic properties may be attributed to the substitution of Fe2+ ions by Mn2+ ions inducing a change in the superexchange interaction between the A and B sublattices. The self-heating characteristics of Mn x Fe1-x Fe2O4 (x = 0-1) nanoparticles (NPs) in an AC magnetic field are evaluated by specific absorption rate (SAR) and intrinsic loss power, both of which are presented with varying NP composition, NP concentration, and field amplitudes. Mn0.75Fe0.25Fe2O4 exhibited superior induction heating properties in terms of a SAR of 153.76 W/g. This superior value of SAR with an optimized Mn2+ content is presented in correlation with the cation distribution of Mn2+ in the A or B position in the Fe3O4 structure and enhancement in magnetic saturation. These optimized Mn0.75Fe0.25Fe2O4 NPs can be used as a promising candidate for hyperthermia applications.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures






References
-
- Doaga A.; Cojocariu A. M.; Amin W.; Heib F.; Bender P.; Hempelmann R.; Caltun O. F. Synthesis and Characterizations of Manganese Ferrites for Hyperthermia Applications. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 143, 305–310. 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.08.066. - DOI
-
- Tabatabai Yazdi S.; Iranmanesh P.; Saeednia S.; Mehran M. Structural, Optical and Magnetic Properties of MnxFe3–xO4 Nanoferrites Synthesized by a Simple Capping Agent-Free Coprecipitation Route. Mater. Sci. Eng., B 2019, 245, 55–62. 10.1016/j.mseb.2019.05.009. - DOI
-
- Rajagiri P.; Sahu B. N.; Venkataramani N.; Prasad S.; Krishnan R. Effect of Substrate Temperature on Magnetic Properties of MnFe2O4 Thin Films. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 056112.10.1063/1.5007792. - DOI
-
- Khot V. M.; Salunkhe A. B.; Phadatare M. R.; Pawar S. H. Formation, Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Nanocrystalline MgFe2O4. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 132, 782–787. 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2011.12.012. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

