Unstable jefferson burst fractures (JBF): Intraoperative stability testing after posterior atlas ring osteosynthesis (C1-RO) allows determination of surgical procedure extent
- PMID: 36506288
- PMCID: PMC9729808
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bas.2022.101668
Unstable jefferson burst fractures (JBF): Intraoperative stability testing after posterior atlas ring osteosynthesis (C1-RO) allows determination of surgical procedure extent
Abstract
Introduction: Motion preserving atlas ring osteosynthesis (C1-RO) for unstable Jefferson burst fractures (JBF) with insufficiency of the transverse atlantal ligament (TAL) is under debate. There is controversy about when to apply C1-RO and when further stabilization is needed.
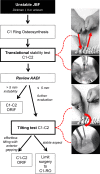
Research question: Is intraoperative stability testing after C1-RO with restoration of secondary stabilizers feasible, and what are mid-to long-term results of posterior C1-RO vs. C1-C2 ORIF in unstable Jefferson burst fractures with Dickman type I or II transverse atlantal ligament lesions based on intraoperative decision using this stability testing?
Material and methods: Five consecutive patients with unstable JBF were treated with posterior C1-RO or C1-C2 ORIF based on the findings after intraoperative reduction and posterior C1-RO and stability testing. This newly developed intraoperative stability test based on the findings of biomechanical studies is a fluoroscopically controlled manual C1-C2 test with a force of approximately 50 N posterior-anterior stress and a tilting maneuver after C1-RO with repositioning. Clinical and radiological results of the cases with C1-RO were analyzed 3.5-21 months postoperatively.
Results: Posterior C1-RO was performed in four patients. One case required C1-C2 fixation due to significant instability. In cases of C1-RO, stable bony fusions of the atlas ring were observed within a year. In flexion-extension views, the anterior atlanto-dental interval (AADI) did not increase until the latest follow-up. No complications were observed.
Discussion and conclusion: The described intraoperative stability test after posterior C1-RO in unstable JBF enables the determination if C1-RO is sufficient or C1-C2 ORIF is necessary for treatment.
Keywords: C1-RO; C1-ring osteosynthesis; Intraoperative stability test; Motion preserving; Unstable jefferson burst fracture.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







References
-
- Abeloos L., De Witte O., Walsdorff M., Delpierre I., Bruneau M. Posterior osteosynthesis of the atlas for nonconsolidated Jefferson fractures: a new surgical technique. Spine. 2011;36(20):E1360–E1363. - PubMed
-
- Böhm H., Kayser R., El Saghir H., Heyde C.E. Die direkte Osteosynthese instabiler Atlasfrakturen Gehweiler Typ III. Präsentation einer dorsoventralen funktionserhaltenden Osteosynthese instabiler Atlasfrakturen [Direct osteosynthesis of instable Gehweiler Type III atlas fractures. Presentation of a dorsoventral osteosynthesis of instable atlas fractures while maintaining function] Unfallchirurg. Sep. 2006;109(9):754–760. doi: 10.1007/s00113-006-1081-x. German, PMID: 16874483. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chung S.K., Park J.T., Lim J., Park J. Open posterior reduction and stabilization of a C1 burst fracture using mono-axial screws. Spine. 2011;36(5):E301–E306. - PubMed
-
- Dickman C.A.C., Mamourian A.A., Sonntag V.K.V., et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the transverse atlantal ligament for the evaluation of atlantoaxial instability. J. Neurosurg. 1991;75:221–227. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

