The role of IL-6 in coronavirus, especially in COVID-19
- PMID: 36506506
- PMCID: PMC9727200
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1033674
The role of IL-6 in coronavirus, especially in COVID-19
Abstract
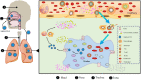
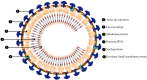
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infects both people and animals and may cause significant respiratory problems, including lung illness: Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Swabs taken from the throat and nose of people who have the illness or are suspected of having it have shown this pathogenic virus. When SARS-CoV-2 infects the upper and lower respiratory tracts, it may induce moderate to severe respiratory symptoms, as well as the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin 6 (IL-6). COVID-19-induced reduction of IL-6 in an inflammatory state may have a hitherto undiscovered therapeutic impact. Many inflammatory disorders, including viral infections, has been found to be regulated by IL-6. In individuals with COVID-19, one of the primary inflammatory agents that causes inflammatory storm is IL-6. It promotes the inflammatory response of virus infection, including the virus infection caused by SARS-CoV-2, and provides a new diagnostic and therapeutic strategy. In this review article, we highlighted the functions of IL-6 in the coronavirus, especially in COVID-19, showing that IL-6 activation plays an important function in the progression of coronavirus and is a rational therapeutic goal for inflammation aimed at coronavirus.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL-6; MERS; SARS; coronavirus.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Tang, Liu, Zhang, Chen, Han, Fu, Wang, Hu, Ma, Sheng, Wang, Hu and Shao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Al-Qahtani A. A., Lyroni K., Aznaourova M., Tseliou M., Al-Anazi M. R., Al-Ahdal M. N., et al. (2017). Middle East respiratory syndrome corona virus spike glycoprotein suppresses macrophage responses via DPP4-mediated induction of IRAK-M and PPARγ. Oncotarget 8 (6), 9053–9066. 10.18632/oncotarget.14754 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baran P., Hansen S., Waetzig G. H., Akbarzadeh M., Lamertz L., Huber H. J., et al. (2018). The balance of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-6.soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R), and IL-6.sIL-6R.sgp130 complexes allows simultaneous classic and trans-signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 293 (18), 6762–6775. 10.1074/jbc.RA117.001163 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

