Exploration of the effect of Celastrol on protein targets in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental evaluations
- PMID: 36506508
- PMCID: PMC9726908
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.996728
Exploration of the effect of Celastrol on protein targets in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental evaluations
Abstract
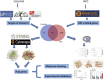
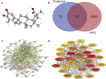
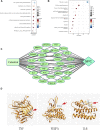
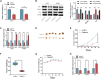
Background: Celastrol, an important extract of Tripterygium wilfordii, shows strong antitumor activity in a variety of tumors including nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). However, little is known about its targets in NPC. We aimed to screen the key gene targets of Celastrol in the treatment of NPC by means of in silico analyses (including network pharmacology and molecular docking) and experimental evaluations. Methods: The main target genes of Celastrol and the genes related to NPC were obtained by retrieving the relevant biological databases, and the common targets were screened. Protein-protein interaction analysis was used to screen the hub genes. Then, a "compound-target-disease" network model was created and molecular docking was used to predict the binding of Celastrol to the candidate hub proteins. Afterward, the expression changes of the candidate genes under the administration of Celastrol were verified in vitro and in vivo. Results: Sixty genes common to Celastrol and NPC were screened out, which may be related to numerous biological processes such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, and tube development, and enriched in various pathways such as PI3K- Akt, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance, and Apoptosis. The tight binding ability of the candidate hub proteins (TNF, VEGFA, and IL6) to Celastrol was predicted by molecular docking [Docking energy: TNF, -6.08; VEGFA,-6.76; IL6,-6.91(kcal/mol)]. In vitro experiments showed that the expression of TNF and VEGFA decreased while the expression of IL6 increased in NPC cells (CNE2 and HONE1) treated with Celastrol. In vivo experiments suggested that Celastrol significantly reduced the weight and volume of the transplanted tumors in tumor-bearing mice in vivo. The expression of TNF, VEGFA, and IL6 in the transplanted tumor cells could be regulated by using Celastrol, and the expression trends were consistent with the in vitro model. Conclusion: Several gene targets have been filtered out as the core targets of Celastrol in the treatment of NPC, which might be involved in a variety of signaling pathways. Hence, Celastrol may exert its anti-NPC activity through multiple targets and multiple pathways, which will provide new clues for further research. Future experiments are warranted to validate the findings.
Keywords: Celastrol; drug targets; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; network pharmacolgy; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2022 Ling, Huang, Sun, Guo, Chang, Pan and Zhuo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The mechanisms of celastrol in treating papillary thyroid carcinoma based on network pharmacology and experiment verification.Ann Transl Med. 2021 May;9(10):866. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-1854. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34164500 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation to Explore That Celastrol Targeting PTEN is the Potential Mechanism of Tripterygium wilfordii (Lév.) Hutch Against IgA Nephropathy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Mar 23;17:887-900. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S402503. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 36992900 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology analysis combined with experimental validation to explore the therapeutic mechanism of Schisandra Chinensis Mixture on diabetic nephropathy.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Feb 10;302(Pt A):115768. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115768. Epub 2022 Oct 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36280016
-
Network pharmacology and experimental verification-based strategy for exploring the mechanisms of luteolin in the treatment of osteosarcoma.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Sep 25;23(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03046-x. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37749554 Free PMC article.
-
The Promising Therapeutic Potential of Celastrol for Fibrotic Diseases: A Systematic Literature Review on Its Mechanism.Cureus. 2023 Aug 28;15(8):e44269. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44269. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37772226 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Network pharmacology: an efficient but underutilized approach in oral, head and neck cancer therapy-a review.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 5;15:1410942. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1410942. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39035991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leaf Extract of Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt Promotes Adipocyte Browning via the p38 MAPK Pathway and PI3K-AKT Pathway.Nutrients. 2023 Mar 20;15(6):1487. doi: 10.3390/nu15061487. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36986217 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

