Application of herbal traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of lupus nephritis
- PMID: 36506523
- PMCID: PMC9729561
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.981063
Application of herbal traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of lupus nephritis
Abstract
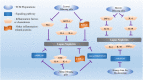
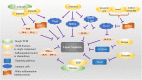
Lupus nephritis (LN) is a secondary renal disease caused by systemic lupus erythematosus affecting the kidneys. It is one of the main causes of end-stage renal disease and a serious risk factor for early mortality and disability of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Existing LN treatment is mainly based on hormones, cytotoxic drugs, and biological agents. Nevertheless, the prognosis of LN patients remains poor because of frequent recurrence and exacerbation of adverse drug reactions. Hence, LN is still the most important cause of end-stage renal disease. In recent years, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has attracted increasing attention because of encouraging evidence that it alleviates LN and the well-described mechanisms underlying renal injury. TCM has therapeutic benefits for treating LN patients. This review article elucidates TCM preparations, TCM monomers, and herbal or natural extraction for LN treatment to provide effective supplementary evidence for promoting the development of TCM treatment for LN and reference for future research and clinical practice.
Keywords: inflammation; kidney injury; lupus nephritis (LN); therapy; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Zhang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources