Associations of HLA-A and HLA-B with vancomycin-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms in the Han-Chinese population
- PMID: 36506572
- PMCID: PMC9732226
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.954596
Associations of HLA-A and HLA-B with vancomycin-induced drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms in the Han-Chinese population
Abstract
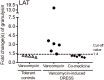
Vancomycin is a commonly used antibiotic; however, it can cause life-threatening severe cutaneous adverse reactions, such as drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS). A previous study has reported a strong association between HLA-A*32:01 and vancomycin-induced DRESS in European ethnicity. Herein, we aim to investigate the genetic predisposition of vancomycin-induced DRESS in the Han-Chinese population. In this study, we enrolled a total of 26 patients with vancomycin-induced DRESS, 1,616 general population controls, and 51 subjects tolerant to vancomycin. In vitro granulysin-based lymphocyte activation tests (LAT) were conducted among 6 vancomycin-induced DRESS patients who were concomitantly receiving other medicines. HLA-A and HLA-B genotypes were determined by sequencing-based typing. Our results found that vancomycin-induced DRESS was associated with HLA-A*32:01 [odds ratio (OR) = 7.8, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.7-35.8; p-value = 0.035], HLA-B*07:05 (OR = 32.3, 95% CI = 2.8-367.7; p-value = 0.047), HLA-B*40:06 (OR = 4.7, 95% CI = 1.3-16.1; p-value = 0.036) and HLA-B*67:01 (OR = 44.8, 95% CI = 7.2-280.4; p-value = 0.002) when comparing the vancomycin-induced DRESS patients with the general population controls. LAT results showed that granulysin significantly increased in the vancomycin-induced DRESS patients upon vancomycin stimulation (4.7 ± 3.7 fold increased), but not upon other co-medicines. This study identified that, in addition to HLA-A*32:01, HLA-B*07:05, HLA-B*40:06, and HLA-B*67:01 were also genetic markers for vancomycin-induced DRESS in the Han-Chinese population. Associations of ethnic variances in HLA with vancomycin-DRESS were observed.
Keywords: HLA; delayed-type drug hypersensitivity reactions; drug reaction with eosinophilia and systematic symptoms; severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions; vancomycin.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Lin, Chen, Chen, Lu, Hou, Hui, Wu, Chang, Chang and Chung.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

