Antibacterial efficacy, calcium ion release, and pH using calcium hydroxide with three vehicles
- PMID: 36506629
- PMCID: PMC9733545
- DOI: 10.4103/jcd.jcd_242_22
Antibacterial efficacy, calcium ion release, and pH using calcium hydroxide with three vehicles
Abstract
Context: Vehicles combined with calcium hydroxide, as an intracanal medicament, play a key factor in affecting antibacterial, calcium release, and pH.
Aims: The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of three vehicles (glycerin, chlorhexidine gluconate/CHX, and chitosan nanoparticle) combined with calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament on antibacterial efficacy against Enterococcus faecalis, calcium ion release, and pH of at different interval times of 7 and 14 days.
Settings and design: The research was experimental laboratory.
Materials and methods: Each study used 24 samples of eight teeth each and was randomly divided into three groups based on the vehicle of calcium hydroxide: group 1: glycerin, group 2: CHX, and group 3: chitosan nanoparticles. Each vehicle group was then further divided into two subgroups of four teeth based on the interval times (group A: 7 days and group B: 14 days). The antibacterial efficacy was determined using an agar diffusion method. Calcium ion release was analyzed with atomic absorption spectrometry, and pH was measured using a pH meter.
Statistical analysis used: Data from each study were analyzed by two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's test with a significance level of 95%.
Results: The results exhibited that chitosan nanoparticles had the highest antibacterial efficacy against E. faecalis, calcium ion release, and pH, while the lowest was glycerin at 7 and 14 days (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Calcium hydroxide combined with chitosan nanoparticle as an intracanal medicament produced the highest antibacterial efficacy against E. faecalis, calcium ion release, and pH than glycerin and CHX at intervals of 7 and 14 days.
Keywords: Antibacterial; calcium hydroxide; calcium ion release; intracanal medicament; pH.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Conservative Dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

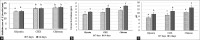

References
-
- Garg A, Garg N. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publisher; 2014. Textbook of Endodontic. 3th ed.
-
- Hussein MM, Abdallah AM, Mokhles NA, Meheissen MA. An ex vivo study to determine the antibacterial efficacy of chitosan nanoparticles, calcium hydroxide and double antibiotic paste as intracanal medicaments against Entrococcus faecalis biofilm. ENDO. 2019;13:255–63.
-
- Del Carpio-Perochena A, Kishen A, Felitti R, Bhagirath AY, Medapati MR, Lai C, et al. Antibacterial properties of chitosan nanoparticles and propolis associated with calcium hydroxide against single- and multispecies biofilms: An in vitro and in situ study. J Endod. 2017;43:1332–6. - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, Tamanna S, Iftekhar H. Intracanal medicaments-their use in modern endodontics. A narrative review. J Oral Res Rev. 2019;11:89–94.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
