Acute and Subchronic Toxicity Studies on the Aqueous Extract of the Plant Mixture (Bidens pilosa and Cymbopogon citratus Aerial Parts) in Rat Model
- PMID: 36506716
- PMCID: PMC9733988
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1998433
Acute and Subchronic Toxicity Studies on the Aqueous Extract of the Plant Mixture (Bidens pilosa and Cymbopogon citratus Aerial Parts) in Rat Model
Abstract
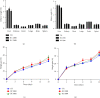
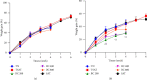
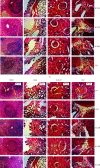
Bidens pilosa (B. pilosa) and Cymbopogon citratus (C. citratus) are plants used individually or in combination in the traditional treatment of several ailments such as cardiovascular disorders. In order to valorise their traditional use, a toxicological study was conducted on the aqueous extract of the mixture of aerial parts of B. pilosa and C. citratus. The acute and subchronic toxicity studies were conducted according to the OECD 425 and 407 guidelines. Regarding the acute study, the aqueous extract of the mixture of B. pilosa and C. citratus 50 : 50 (2000 and 5000 mg/kg) was administered once to rats of both sexes. In the subchronic study, the aqueous extract of the mixture of B. pilosa and C. citratus (200, 400 and 800 mg/kg) was administered once daily to rats for 28 days. The aqueous extract of the mixture of B. pilosa and C. citratus (2000 and 5000 mg/kg) did not cause death and did not induce any apparent sign of toxicity during the 14 days of observation. The DL50 of the extract is therefore greater than 5000 mg/kg. Taken daily for 28 days, the extract had no significant effect on selected parameters (creatinine, AST, ALT, urea, and uric acid) of renal and hepatic function, as well as on the number of some blood cells. However, the aqueous extract of the mixture of B. pilosa and C. citratus (200 and 400 mg/kg) caused a significant (p < 0.05; p < 0.001, respectively) decrease in creatinine levels in male rats as compared to normal control animals. In females, the aqueous extract of the mixture of B. pilosa and C. citratus (200 and 400 mg/kg) resulted in a significant (p < 0.05) increase in total cholesterol levels as compared to normal control animals. The study showed that the aqueous extract of the mixture of B. pilosa and C. citratus has a low toxicity and does not cause any injury to the liver, kidney, lungs, or spleen.
Copyright © 2022 Yannick Carlos Tcheutchoua et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in the present research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preventive Potential of the Aqueous Extract of the Mixture of Bidens pilosa (Asteraceae) and Cymbopogon citratus (Poaceae) Aerial Parts on Hypertension Induced by a Chronic Salt and Alcohol Consumption on the Rats.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Mar 9;2022:1980622. doi: 10.1155/2022/1980622. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35310038 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and Subchronic Toxicity Assessment of Conventional Soxhlet Cymbopogon citratus Leaves Extracts in Sprague-Dawley Rats.J Toxicol. 2023 Dec 11;2023:8575741. doi: 10.1155/2023/8575741. eCollection 2023. J Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 38111630 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatoprotective effect of Cymbopogon citratus aqueous extract against hydrogen peroxide-induced liver injury in male rats.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jan 28;11(2):447-51. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v11i2.31. eCollection 2014. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25435631 Free PMC article.
-
A Bidens pilosa L. Non-Polar Extract Modulates the Polarization of Human Macrophages and Dendritic Cells into an Anti-Inflammatory Phenotype.Molecules. 2023 Oct 14;28(20):7094. doi: 10.3390/molecules28207094. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37894572 Free PMC article.
-
Cymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf mitigates ER-stress induced by streptozotocin in rats via down-regulation of GRP78 and up-regulation of Nrf2 signaling.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Nov 15;262:113130. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113130. Epub 2020 Jul 28. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32736056
Cited by
-
Acute and subchronic toxicity of aqueous extracts of Combretum micranthum (G. Don) and Gardenia sokotensis (Hutch) having ethnobotanical uses in Burkina Faso.Toxicol Rep. 2025 Jul 28;15:102097. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2025.102097. eCollection 2025 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40778320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organisation mondiale de la santé. Stratégie de l’OMS pour la médecine traditionnelle pour 2014-2023 . Suisse: Genève; 2013. p. p. 75.
-
- Silva J. C., Souza P. S. M., Aragão F., et al. Vasorelaxant activity and acute toxicity of the ethanolic extract of Zanthoxylum rhoifolium Lam leaves. Brazilian J. Pharm. Sci. . 2019;55:p. 17754. doi: 10.1590/S2175-97902019000117754. - DOI
-
- Yinyang Jacques T. S. E., Mvogo Ottou Patrice Brice B. H. D., Ngouondjou Foze Teclaire N. H. J. M., et al. Acute and Subacute toxicity Studies of the combination of the aqueous extracts of trunk bark of Musanga cecropioides R. Br. (Cecropiaceae) and fruits of Picralima nitida (Stapf) T. Durand and H. Durand (Apocynaceae) Saudi Journal of Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences . 2020;06(04):334–348. doi: 10.36348/sjmps.2020.v06i04.002. - DOI
-
- Ukwuani A., Abubakar M., Hassan S., Agaie B. Toxicological studies of hydromethanolic leaves extract of Grewia crenata. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Drug Research . 2012;4(4):245–249.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

