An effective deep learning approach for the classification of Bacteriosis in peach leave
- PMID: 36507379
- PMCID: PMC9730539
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1064854
An effective deep learning approach for the classification of Bacteriosis in peach leave
Abstract
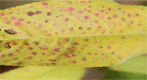
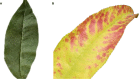
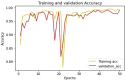
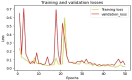
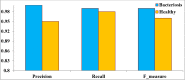
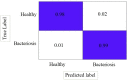
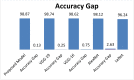
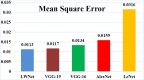
Bacteriosis is one of the most prevalent and deadly infections that affect peach crops globally. Timely detection of Bacteriosis disease is essential for lowering pesticide use and preventing crop loss. It takes time and effort to distinguish and detect Bacteriosis or a short hole in a peach leaf. In this paper, we proposed a novel LightWeight (WLNet) Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model based on Visual Geometry Group (VGG-19) for detecting and classifying images into Bacteriosis and healthy images. Profound knowledge of the proposed model is utilized to detect Bacteriosis in peach leaf images. First, a dataset is developed which consists of 10000 images: 4500 are Bacteriosis and 5500 are healthy images. Second, images are preprocessed using different steps to prepare them for the identification of Bacteriosis and healthy leaves. These preprocessing steps include image resizing, noise removal, image enhancement, background removal, and augmentation techniques, which enhance the performance of leaves classification and help to achieve a decent result. Finally, the proposed LWNet model is trained for leaf classification. The proposed model is compared with four different CNN models: LeNet, Alexnet, VGG-16, and the simple VGG-19 model. The proposed model obtains an accuracy of 99%, which is higher than LeNet, Alexnet, VGG-16, and the simple VGG-19 model. The achieved results indicate that the proposed model is more effective for the detection of Bacteriosis in peach leaf images, in comparison with the existing models.
Keywords: Bacteriosis classification; Bacteriosis detection; LWNet; convolutional neural network (CNN); deep learning; peach leaves.
Copyright © 2022 Akbar, Ullah, Shah, Khan, Hussain, Ali, Alenezi, Syed and Kwak.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ahila Priyadharshini R., Arivazhagan S., Arun M., Mirnalini A. (2019). Maize leaf disease classification using deep convolutional neural networks. Neural Comput Appl. 31 (12), 8887–8895. doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04228-3 - DOI
-
- Alehegn E. (2019). Ethiopian Maize diseases recognition and classification using support vector machine. Int. J. Comput. Vision Robot 9 (1), 90–109. doi: 10.1504/IJCVR.2019.098012 - DOI
-
- Behera S. K., Jena L., Rath A. K., Sethy P. K. (2018). “Disease classification and grading of orange using machine learning and fuzzy logic,” in 2018 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP) (India:IEEE; ). 0678–0682 (IEEE). doi: 10.1109/ICCSP.2018.8524415 - DOI
-
- da Costa A. Z., Figueroa H. E., Fracarolli J. A. (2020). Computer vision based detection of external defects on tomatoes using deep learning. Biosyst. Eng. 190, 131–144. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2019.12.003 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

