Translation and Validation of the Dysphagia Handicap Index in Polish-Speaking Patients
- PMID: 36507957
- PMCID: PMC10326088
- DOI: 10.1007/s00455-022-10545-y
Translation and Validation of the Dysphagia Handicap Index in Polish-Speaking Patients
Abstract
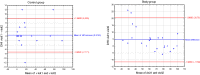
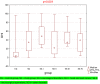
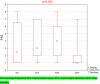
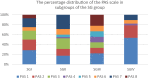
Dysphagia Handicap Index (DHI) is a self-assessment questionnaire which consists of 25 statements to examine three aspects of dysphagia patients' quality of life (QoL): functional, physical, and emotional. The patient can get a maximum score of 100 points. The study goal was to validate and translate the Polish version of the DHI (PL-DHI). One hundred and seventy-eight (178) individuals with oropharyngeal dysphagia with different etiology and 35 (thirty-five) asymptomatic adults with no history of swallowing disorders filled out the PL-DHI. Internal consistency was determined using Cronbach alpha coefficient, which was high for the total PL-DHI score (0.962). The reproducibility was high (r-Spearman correlation coefficient was 0.97 for total PL-DHI score). The PL-DHI's total score and its subscales were significantly higher in the dysphagia patients study group (SG) than in the healthy controls group (CG) (SG median: 36; CG median: 4). A strong correlation was observed between the PL-DHI score and the self-reported dysphagia severity measure (Spearman's correlation coefficient was 0.859, p < 0.001). The Polish DHI is a reliable and valid questionnaire for assessing dysphagia patients' QoL.
Keywords: DHI; Deglutition; Deglutition disorders; Dysphagia; Dysphagia Handicap Index; Oropharyngeal dysphagia; Quality of life.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Ewelina M. Sielska-Badurek, Maria Sobol, Joanna Chmielewska-Walczak, Barbara Jamróz, and Kazimierz Niemczyk report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Translation and Validation of the Dysphagia Handicap Index in Hebrew-Speaking Patients.Dysphagia. 2019 Feb;34(1):63-72. doi: 10.1007/s00455-018-9914-7. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Dysphagia. 2019. PMID: 29882103
-
Translation and Validation of Kannada Version of the Dysphagia Handicap Index.Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2020 Feb 7;29(1):255-262. doi: 10.1044/2019_AJSLP-19-00122. Epub 2020 Jan 15. Am J Speech Lang Pathol. 2020. PMID: 31940224
-
Cross-Cultural Adaptation and Validation of the Italian Version of the Dysphagia Handicap Index (I-DHI).Dysphagia. 2022 Oct;37(5):1120-1136. doi: 10.1007/s00455-021-10369-2. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Dysphagia. 2022. PMID: 34581857 Free PMC article.
-
Cultural Adaptation and Validation of Questionnaires for Evaluation of Health-Related Quality of Life with Dysphagia in Different Countries: A Systematic Review.Dysphagia. 2022 Aug;37(4):812-823. doi: 10.1007/s00455-021-10330-3. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Dysphagia. 2022. PMID: 34181064
-
The Dysphagia Handicap Index (DHI)-Normative Values. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Dysphagia. 2021 Dec;36(6):1005-1009. doi: 10.1007/s00455-020-10231-x. Epub 2021 Jan 1. Dysphagia. 2021. PMID: 33386481
Cited by
-
Impact of Modified Diet, Swallowing Exercises, and Electrostimulation on Quality of Life of Older Patients Suffering from Oropharyngeal Dysphagia.Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Jun 21;60(7):1021. doi: 10.3390/medicina60071021. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39064450 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and Validity of the Chinese Mandarin Version of the Dysphagia Handicap Index.Dysphagia. 2025 Apr;40(2):419-430. doi: 10.1007/s00455-024-10744-9. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Dysphagia. 2025. PMID: 39096333
References
-
- Warnecke T, Dziwas R, Langmore S. Neurogenic dysphagia. New York: Spinger; 2021. p. 8.
-
- Garcia-Peris P, Parón L, Velasco C, de la Cuerda C, Camblo M, Breton I, Herencia H, Verdaguer J, Navarro C, Clave P. Long-term prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in head and neck cancer patients: Impact on quality of life. Clin Nutr. 2007;26:710–717. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2007.08.006. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

