MicroRNAs: key regulators of the trophoblast function in pregnancy disorders
- PMID: 36508034
- PMCID: PMC9742672
- DOI: 10.1007/s10815-022-02677-9
MicroRNAs: key regulators of the trophoblast function in pregnancy disorders
Abstract
The placenta is essential for a successful pregnancy and healthy intrauterine development in mammals. During human pregnancy, the growth and development of the placenta are inseparable from the rapid proliferation, invasion, and migration of trophoblast cells. Previous reports have shown that the occurrence of many pregnancy disorders may be closely related to the dysfunction of trophoblasts. However, the function regulation of human trophoblast cells in the placenta is poorly understood. Therefore, studying the factors that regulate the function of trophoblast cells is necessary. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, non-coding, single-stranded RNA molecules. Increasing evidence suggests that miRNAs play a crucial role in regulating trophoblast functions. This review outlines the role of miRNAs in regulating the function of trophoblast cells and several common signaling pathways related to miRNA regulation in pregnancy disorders.
Keywords: MicroRNAs; Placenta; Pregnancy disorders; Trophoblast cells.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

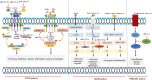
References
-
- Turco MY and Moffett A Development of the human placenta. Dev. 2019;146(22). 10.1242/dev.163428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 81970389/the Natural Science Foundation of China
- Grant No.2021JJ30626/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- 2022JJ30533/Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province
- Grant No.18B283/Scientific Research Project of Hunan Provincial Department of Education
- 2022JJ30038/Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province for Distinguished Young Scholars
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

