The Global, Regional, and National Burden and Trends of NAFLD in 204 Countries and Territories: An Analysis From Global Burden of Disease 2019
- PMID: 36508249
- PMCID: PMC9793331
- DOI: 10.2196/34809
The Global, Regional, and National Burden and Trends of NAFLD in 204 Countries and Territories: An Analysis From Global Burden of Disease 2019
Abstract
Background: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) poses a substantial socioeconomic burden and is becoming the fastest growing driver of chronic liver disease, potentially accompanied by a poor prognosis.
Objective: We aim to elucidate the global and regional epidemiologic changes in NAFLD during the past 30 years and explore the interconnected diseases.
Methods: Data on NAFLD incidence, prevalence, death, and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) were extracted from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The age-standardized incident rate (ASIR), age-standardized prevalent rate (ASPR), age-standardized death rate (ASDR), and age-standardized DALYs were calculated to eliminate the confounding effects of age when comparing the epidemiologic changes between different geographical regions. In addition, we also investigated the correlation between the NAFLD burden and the sociodemographic index (SDI). Finally, the associations of the 3 common comorbidities with NAFLD were determined.
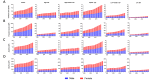
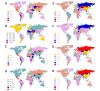
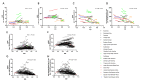
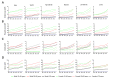
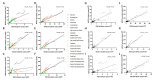
Results: Globally, the incidence and prevalence of NAFLD both increased drastically during the past 3 decades (incidence: from 88,180 in 1990 to 172,330 in 2019, prevalence: from 561,370,000 in 1990 to 1,235,700,000 in 2019), mainly affecting young adults who were aged from 15 to 49 years. The ASIR increased slightly from 1.94 per 100,000 population in 1990 to 2.08 per 100,000 population in 2019, while ASPR increased from 12,070 per 100,000 population in 1990 to 15,020 per 100,000 population in 2019. In addition, the number of deaths and DALYs attributable to NAFLD increased significantly as well from 93,760 in 1990 to 168,970 in 2019 and from 2,711,270 in 1990 to 4,417,280 in 2019, respectively. However, the ASDR and age-standardized DALYs presented decreasing trends with values of estimated annual percentage change equaling to -0.67 and -0.82, respectively (ASDR: from 2.39 per 100,000 population in 1990 to 2.09 per 100,000 population in 2019; age-standardized DALYs: from 63.28 per 100,000 population in 1990 to 53.33 per 100,000 population in 2019). Thereinto, the burden of death and DALYs dominated the patients with NAFLD who are older than 50 years. Moreover, SDI appeared to have obvious negative associations with ASPR, ASDR, and age-standardized DALYs among 21 regions and 204 countries, although there is no marked association with ASIR. Finally, we found that the incidence and prevalence of NAFLD were positively related to those of diabetes mellitus type 2, stroke, and ischemic heart disease.
Conclusions: NAFLD is leading to increasingly serious health challenges worldwide. The morbidity presented a clear shift toward the young populations, while the heavier burden of death and DALYs in NAFLD was observed in the aged populations and in regions with relatively low SDI. Comprehensive acquisition of the epidemiologic pattern for NAFLD and the identification of high-risk comorbidities may help policy makers and clinical physicians develop cost-effective prevention and control strategies, especially in countries with a high NAFLD burden.
Keywords: Global Burden of Disease Study 2019; diabetes mellitus type 2; disability-adjusted life-years; epidemiologic change; incidence; ischemic heart disease; mortality; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; prevalence; stroke.
©Huilong Chen, Yuan Zhan, Jinxiang Zhang, Sheng Cheng, Yuhao Zhou, Liyuan Chen, Zhilin Zeng. Originally published in JMIR Public Health and Surveillance (https://publichealth.jmir.org), 12.12.2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Sanyal AJ, Brunt EM, Kleiner DE, Kowdley KV, Chalasani N, Lavine JE, Ratziu V, McCullough A. Endpoints and clinical trial design for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2011 Jul;54(1):344–353. doi: 10.1002/hep.24376. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/21520200 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Golabi P, Paik JM, AlQahtani S, Younossi Y, Tuncer G, Younossi ZM. Burden of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, the Middle East and North Africa: data from Global Burden of Disease 2009-2019. J Hepatol. 2021 Oct;75(4):795–809. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.05.022.S0168-8278(21)00358-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Charlton M, Cusi K, Rinella M, Harrison SA, Brunt EM, Sanyal AJ. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018 Jan;67(1):328–357. doi: 10.1002/hep.29367. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

