Pterin-based small molecule inhibitor capable of binding to the secondary pocket in the active site of ricin-toxin A chain
- PMID: 36508422
- PMCID: PMC9744275
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277770
Pterin-based small molecule inhibitor capable of binding to the secondary pocket in the active site of ricin-toxin A chain
Erratum in
-
Correction: Pterin-based small molecule inhibitor capable of binding to the secondary pocket in the active site of ricin-toxin A chain.PLoS One. 2024 May 17;19(5):e0304251. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304251. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38758801 Free PMC article.
Abstract
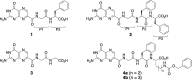
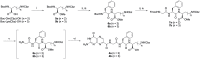
The Ricin toxin A chain (RTA), which depurinates an adenine base at a specific region of the ribosome leading to death, has two adjacent specificity pockets in its active site. Based on this structural information, many attempts have been made to develop small-molecule RTA inhibitors that simultaneously block the two pockets. However, no attempt has been successful. In the present study, we synthesized pterin-7-carboxamides with tripeptide pendants and found that one of them interacts with both pockets simultaneously to exhibit good RTA inhibitory activity. X-ray crystallographic analysis of the RTA crystal with the new inhibitor revealed that the conformational change of Tyr80 is an important factor that allows the inhibitors to plug the two pockets simultaneously.
Copyright: © 2022 Saito et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Endo Y, Chan YL, Lin A, Tsurugi K, Wool IG. The cytotoxins α-sarcin and ricin retain their specificity when tested on a synthetic oligoribonucleotide (35-Mer) that mimics a region of 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1988;263(17):7917–20. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)68418-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

